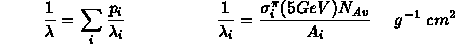
For a compound ( NLMAT < 0), the molecular weight and charge are:
where = WMAT(I) is the number of atoms of the
component of the molecule. In this case the proportion by weight is:
where = WMAT(I) in output. From the relative weights, GSMIXT works out the effective atomic weight and atomic number according to the following formulas:
which are stored in the JMATE data structure [CONS199] together with the radiation length.
The radiation length is computed according to the EGS manual [], formula 268 (37), for an element:
where
for a compound or mixture:
where is the proportion by weight of the element. For more information on the organisation of the data in memory see [CONS199].
The effective absorption length is defined as the interaction length of a 5GeV pion in the material:
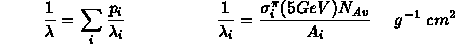
Once this value has been determined, an effective hadronic atomic weight ( ) is calculated by the routine GHMIX [] and stored in the data structure.
R.Brun, M.Maire CONS199