// @(#)root/base:$Name: $:$Id: TMath.cxx,v 1.5 2000/06/30 09:02:57 rdm Exp $
// Author: Fons Rademakers 29/07/95
/*************************************************************************
* Copyright (C) 1995-2000, Rene Brun and Fons Rademakers. *
* All rights reserved. *
* *
* For the licensing terms see $ROOTSYS/LICENSE. *
* For the list of contributors see $ROOTSYS/README/CREDITS. *
*************************************************************************/
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// //
// TMath //
// //
// Encapsulate math routines (i.e. provide a kind of namespace). //
// For the time being avoid templates. //
// //
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
#include "TMath.h"
#include <math.h>
#include <string.h>
//const Double_t
// TMath::Pi = 3.14159265358979323846,
// TMath::E = 2.7182818284590452354;
ClassImp(TMath)
//______________________________________________________________________________
#if defined(R__MAC) || defined(R__KCC)
Double_t hypot(Double_t x, Double_t y) {
return sqrt(x*x+y*y);
}
#endif
//______________________________________________________________________________
Long_t TMath::Sqrt(Long_t x)
{
return (Long_t) (sqrt((Double_t)x) + 0.5);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Long_t TMath::Hypot(Long_t x, Long_t y) // return sqrt(px*px + py*py);
{
return (Long_t) (hypot(x, y) + 0.5);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::Hypot(Double_t x, Double_t y)
{
return hypot(x, y);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::ASinH(Double_t x)
{
#if defined(WIN32) || defined(R__KCC)
return log(x+sqrt(x*x+1));
#else
return asinh(x);
#endif
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::ACosH(Double_t x)
{
#if defined(WIN32) || defined(R__KCC)
return log(x+sqrt(x*x-1));
#else
return acosh(x);
#endif
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::ATanH(Double_t x)
{
#if defined(WIN32) || defined(R__KCC)
return log((1+x)/(1-x))/2;
#else
return atanh(x);
#endif
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::Ceil(Double_t x)
{
return ceil(x);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::Floor(Double_t x)
{
return floor(x);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::Log2(Double_t x)
{
return log(x)/log(2.0);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Long_t TMath::NextPrime(Long_t x)
{
// Return next prime number after x, unless x is a prime in which case
// x is returned.
if (x < 2)
return 2;
if (x == 3)
return 3;
if (x % 2 == 0)
x++;
Long_t sqr = (Long_t) sqrt((Double_t)x) + 1;
for (;;) {
Long_t n;
for (n = 3; (n <= sqr) && ((x % n) != 0); n += 2)
;
if (n > sqr)
return x;
x += 2;
}
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TMath::Nint(Float_t x)
{
int i;
if (x >= 0) {
i = int(x + 0.5);
if (x + 0.5 == Float_t(i) && i & 1) i--;
} else {
i = int(x - 0.5);
if (x - 0.5 == Float_t(i) && i & 1) i++;
}
return i;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TMath::Nint(Double_t x)
{
int i;
if (x >= 0) {
i = int(x + 0.5);
if (x + 0.5 == Double_t(i) && i & 1) i--;
} else {
i = int(x - 0.5);
if (x - 0.5 == Double_t(i) && i & 1) i++;
}
return i;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Float_t *TMath::Cross(Float_t v1[3],Float_t v2[3],Float_t out[3])
{
// Calculate the Cross Product of two vectors
// out = [v1 x v2]
out[0] = v1[1] * v2[2] - v1[2] * v2[1];
out[1] = v1[2] * v2[0] - v1[0] * v2[2];
out[2] = v1[0] * v2[1] - v1[1] * v2[0];
return out;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t *TMath::Cross(Double_t v1[3],Double_t v2[3],Double_t out[3])
{
// Calculate the Cross Product of two vectors
// out = [v1 x v2]
out[0] = v1[1] * v2[2] - v1[2] * v2[1];
out[1] = v1[2] * v2[0] - v1[0] * v2[2];
out[2] = v1[0] * v2[1] - v1[1] * v2[0];
return out;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::Erf(Double_t x)
{
// Computation of the error function erf(x).
//
//--- NvE 14-nov-1998 UU-SAP Utrecht
return (1-Erfc(x));
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::Erfc(Double_t x)
{
// Computation of the complementary error function erfc(x).
//
// The algorithm is based on a Chebyshev fit as denoted in
// Numerical Recipes 2nd ed. on p. 214 (W.H.Press et al.).
//
// The fractional error is always less than 1.2e-7.
//
//--- Nve 14-nov-1998 UU-SAP Utrecht
// The parameters of the Chebyshev fit
const Double_t a1 = -1.26551223, a2 = 1.00002368,
a3 = 0.37409196, a4 = 0.09678418,
a5 = -0.18628806, a6 = 0.27886807,
a7 = -1.13520398, a8 = 1.48851587,
a9 = -0.82215223, a10 = 0.17087277;
Double_t v = 1; // The return value
Double_t z = Abs(x);
if (z <= 0) return v; // erfc(0)=1
Double_t t = 1/(1+0.5*z);
v = t*Exp((-z*z) +a1+t*(a2+t*(a3+t*(a4+t*(a5+t*(a6+t*(a7+t*(a8+t*(a9+t*a10)))))))));
if (x < 0) v = 2-v; // erfc(-x)=2-erfc(x)
return v;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::Gamma(Double_t z)
{
// Computation of gamma(z) for all z>0.
//
// The algorithm is based on the article by C.Lanczos [1] as denoted in
// Numerical Recipes 2nd ed. on p. 207 (W.H.Press et al.).
//
// [1] C.Lanczos, SIAM Journal of Numerical Analysis B1 (1964), 86.
//
//--- Nve 14-nov-1998 UU-SAP Utrecht
if (z<=0) return 0;
Double_t v = LnGamma(z);
return Exp(v);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::Gamma(Double_t a,Double_t x)
{
// Computation of the incomplete gamma function P(a,x)
//
// The algorithm is based on the formulas and code as denoted in
// Numerical Recipes 2nd ed. on p. 210-212 (W.H.Press et al.).
//
//--- Nve 14-nov-1998 UU-SAP Utrecht
if (a <= 0 || x <= 0) return 0;
if (x < (a+1)) return GamSer(a,x);
else return GamCf(a,x);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::GamCf(Double_t a,Double_t x)
{
// Computation of the incomplete gamma function P(a,x)
// via its continued fraction representation.
//
// The algorithm is based on the formulas and code as denoted in
// Numerical Recipes 2nd ed. on p. 210-212 (W.H.Press et al.).
//
//--- Nve 14-nov-1998 UU-SAP Utrecht
Int_t itmax = 100; // Maximum number of iterations
Double_t eps = 3.e-7; // Relative accuracy
Double_t fpmin = 1.e-30; // Smallest Double_t value allowed here
if (a <= 0 || x <= 0) return 0;
Double_t gln = LnGamma(a);
Double_t b = x+1-a;
Double_t c = 1/fpmin;
Double_t d = 1/b;
Double_t h = d;
Double_t an,del;
for (Int_t i=1; i<=itmax; i++) {
an = Double_t(-i)*(Double_t(i)-a);
b += 2;
d = an*d+b;
if (Abs(d) < fpmin) d = fpmin;
c = b+an/c;
if (Abs(c) < fpmin) c = fpmin;
d = 1/d;
del = d*c;
h = h*del;
if (Abs(del-1) < eps) break;
//if (i==itmax) cout << "*GamCf(a,x)* a too large or itmax too small" << endl;
}
Double_t v = Exp(-x+a*Log(x)-gln)*h;
return (1-v);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::GamSer(Double_t a,Double_t x)
{
// Computation of the incomplete gamma function P(a,x)
// via its series representation.
//
// The algorithm is based on the formulas and code as denoted in
// Numerical Recipes 2nd ed. on p. 210-212 (W.H.Press et al.).
//
//--- Nve 14-nov-1998 UU-SAP Utrecht
Int_t itmax = 100; // Maximum number of iterations
Double_t eps = 3.e-7; // Relative accuracy
if (a <= 0 || x <= 0) return 0;
Double_t gln = LnGamma(a);
Double_t ap = a;
Double_t sum = 1/a;
Double_t del = sum;
for (Int_t n=1; n<=itmax; n++) {
ap += 1;
del = del*x/ap;
sum += del;
if (TMath::Abs(del) < Abs(sum*eps)) break;
//if (n==itmax) cout << "*GamSer(a,x)* a too large or itmax too small" << endl;
}
Double_t v = sum*Exp(-x+a*Log(x)-gln);
return v;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::Gaus(Double_t x, Double_t mean, Double_t sigma)
{
// Calculate a gaussian function with mean and sigma
if (sigma == 0) return 1.e30;
Double_t arg = (x-mean)/sigma;
return TMath::Exp(-0.5*arg*arg);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::Landau(Double_t x, Double_t mean, Double_t sigma)
{
// The LANDAU function with mean and sigma.
// This function has been adapted from the CERNLIB routine G110 denlan.
Double_t p1[5] = {0.4259894875,-0.1249762550, 0.03984243700, -0.006298287635, 0.001511162253};
Double_t q1[5] = {1.0 ,-0.3388260629, 0.09594393323, -0.01608042283, 0.003778942063};
Double_t p2[5] = {0.1788541609, 0.1173957403, 0.01488850518, -0.001394989411, 0.0001283617211};
Double_t q2[5] = {1.0 , 0.7428795082, 0.3153932961, 0.06694219548, 0.008790609714};
Double_t p3[5] = {0.1788544503, 0.09359161662,0.006325387654, 0.00006611667319,-0.000002031049101};
Double_t q3[5] = {1.0 , 0.6097809921, 0.2560616665, 0.04746722384, 0.006957301675};
Double_t p4[5] = {0.9874054407, 118.6723273, 849.2794360, -743.7792444, 427.0262186};
Double_t q4[5] = {1.0 , 106.8615961, 337.6496214, 2016.712389, 1597.063511};
Double_t p5[5] = {1.003675074, 167.5702434, 4789.711289, 21217.86767, -22324.94910};
Double_t q5[5] = {1.0 , 156.9424537, 3745.310488, 9834.698876, 66924.28357};
Double_t p6[5] = {1.000827619, 664.9143136, 62972.92665, 475554.6998, -5743609.109};
Double_t q6[5] = {1.0 , 651.4101098, 56974.73333, 165917.4725, -2815759.939};
Double_t a1[3] = {0.04166666667,-0.01996527778, 0.02709538966};
Double_t a2[2] = {-1.845568670,-4.284640743};
if (sigma <= 0) return 0;
Double_t v = (x-mean)/sigma;
Double_t u, ue, us, den;
if (v < -5.5) {
u = TMath::Exp(v+1.0);
ue = TMath::Exp(-1/u);
us = TMath::Sqrt(u);
den = 0.3989422803*(ue/us)*(1+(a1[0]+(a1[1]+a1[2]*u)*u)*u);
} else if(v < -1) {
u = TMath::Exp(-v-1);
den = TMath::Exp(-u)*TMath::Sqrt(u)*
(p1[0]+(p1[1]+(p1[2]+(p1[3]+p1[4]*v)*v)*v)*v)/
(q1[0]+(q1[1]+(q1[2]+(q1[3]+q1[4]*v)*v)*v)*v);
} else if(v < 1) {
den = (p2[0]+(p2[1]+(p2[2]+(p2[3]+p2[4]*v)*v)*v)*v)/
(q2[0]+(q2[1]+(q2[2]+(q2[3]+q2[4]*v)*v)*v)*v);
} else if(v < 5) {
den = (p3[0]+(p3[1]+(p3[2]+(p3[3]+p3[4]*v)*v)*v)*v)/
(q3[0]+(q3[1]+(q3[2]+(q3[3]+q3[4]*v)*v)*v)*v);
} else if(v < 12) {
u = 1/v;
den = u*u*(p4[0]+(p4[1]+(p4[2]+(p4[3]+p4[4]*u)*u)*u)*u)/
(q4[0]+(q4[1]+(q4[2]+(q4[3]+q4[4]*u)*u)*u)*u);
} else if(v < 50) {
u = 1/v;
den = u*u*(p5[0]+(p5[1]+(p5[2]+(p5[3]+p5[4]*u)*u)*u)*u)/
(q5[0]+(q5[1]+(q5[2]+(q5[3]+q5[4]*u)*u)*u)*u);
} else if(v < 300) {
u = 1/v;
den = u*u*(p6[0]+(p6[1]+(p6[2]+(p6[3]+p6[4]*u)*u)*u)*u)/
(q6[0]+(q6[1]+(q6[2]+(q6[3]+q6[4]*u)*u)*u)*u);
} else {
u = 1/(v-v*TMath::Log(v)/(v+1));
den = u*u*(1+(a2[0]+a2[1]*u)*u);
}
return den;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::LnGamma(Double_t z)
{
// Computation of ln[gamma(z)] for all z>0.
//
// The algorithm is based on the article by C.Lanczos [1] as denoted in
// Numerical Recipes 2nd ed. on p. 207 (W.H.Press et al.).
//
// [1] C.Lanczos, SIAM Journal of Numerical Analysis B1 (1964), 86.
//
// The accuracy of the result is better than 2e-10.
//
//--- Nve 14-nov-1998 UU-SAP Utrecht
if (z<=0) return 0;
// Coefficients for the series expansion
Double_t c[7] = { 2.5066282746310005, 76.18009172947146, -86.50532032941677
,24.01409824083091, -1.231739572450155, 0.1208650973866179e-2
,-0.5395239384953e-5};
Double_t x = z;
Double_t y = x;
Double_t tmp = x+5.5;
tmp = (x+0.5)*Log(tmp)-tmp;
Double_t ser = 1.000000000190015;
for (Int_t i=1; i<7; i++) {
y += 1;
ser += c[i]/y;
}
Double_t v = tmp+Log(c[0]*ser/x);
return v;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Float_t TMath::Normalize(Float_t v[3])
{
// Normalize a vector v in place
// Return:
// The norm of the original vector
Float_t d = Sqrt(v[0]*v[0]+v[1]*v[1]+v[2]*v[2]);
if (d != 0)
{
v[0] /= d;
v[1] /= d;
v[2] /= d;
}
return d;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::Normalize(Double_t v[3])
{
// Normalize a vector v in place
// Return:
// The norm of the original vector
Double_t d = Sqrt(v[0]*v[0]+v[1]*v[1]+v[2]*v[2]);
if (d != 0)
{
v[0] /= d;
v[1] /= d;
v[2] /= d;
}
return d;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Float_t *TMath::Normal2Plane(Float_t p1[3],Float_t p2[3],Float_t p3[3], Float_t normal[3])
{
// Calculate a normal vector of a plane
//
// Input:
// Float_t *p1,*p2,*p3 - 3 3D points belonged the plane to define it.
//
// Return:
// Pointer to 3D normal vector (normalized)
//
Float_t v1[3], v2[3];
v1[0] = p2[0] - p1[0];
v1[1] = p2[1] - p1[1];
v1[2] = p2[2] - p1[2];
v2[0] = p3[0] - p1[0];
v2[1] = p3[1] - p1[1];
v2[2] = p3[2] - p1[2];
NormCross(v1,v2,normal);
return normal;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t *TMath::Normal2Plane(Double_t p1[3],Double_t p2[3],Double_t p3[3], Double_t normal[3])
{
// Calculate a normal vector of a plane
//
// Input:
// Float_t *p1,*p2,*p3 - 3 3D points belonged the plane to define it.
//
// Return:
// Pointer to 3D normal vector (normalized)
//
Double_t v1[3], v2[3];
v1[0] = p2[0] - p1[0];
v1[1] = p2[1] - p1[1];
v1[2] = p2[2] - p1[2];
v2[0] = p3[0] - p1[0];
v2[1] = p3[1] - p1[1];
v2[2] = p3[2] - p1[2];
NormCross(v1,v2,normal);
return normal;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::Prob(Double_t chi2,Int_t ndf)
{
// Computation of the probability for a certain Chi-squared (chi2)
// and number of degrees of freedom (ndf).
//
// Calculations are based on the incomplete gamma function P(a,x),
// where a=ndf/2 and x=chi2/2.
//
// P(a,x) represents the probability that the observed Chi-squared
// for a correct model should be less than the value chi2.
//
// The returned probability corresponds to 1-P(a,x),
// which denotes the probability that an observed Chi-squared exceeds
// the value chi2 by chance, even for a correct model.
//
//--- NvE 14-nov-1998 UU-SAP Utrecht
if (ndf <= 0) return 0; // Set CL to zero in case ndf<=0
if (chi2 <= 0) {
if (chi2 < 0) return 0;
else return 1;
}
if (ndf==1) {
Double_t v = 1.-Erf(Sqrt(chi2)/Sqrt(2.));
return v;
}
// Gaussian approximation for large ndf
Double_t q = Sqrt(2*chi2)-Sqrt(Double_t(2*ndf-1));
if (ndf > 30 && q > 0) {
Double_t v = 0.5*(1-Erf(q/Sqrt(2.)));
return v;
}
// Evaluate the incomplete gamma function
return (1-Gamma(0.5*ndf,0.5*chi2));
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::KolmogorovProb(Double_t z)
{
// Calculates the Kolmogorov distribution function,
//
/*
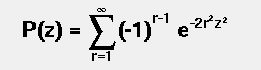 */
//
// which gives the probability that Kolmogorov's test statistic will exceed
// the value z assuming the null hypothesis. This gives a very powerful
// test for comparing two one-dimensional distributions.
// see, for example, Eadie et al, "statistocal Methods in Experimental
// Physics', pp 269-270).
//
// This function returns the confidence level for the null hypothesis, where:
// z = dn*sqrt(n), and
// dn is the maximum deviation between a hypothetical distribution
// function and an experimental distribution with
// n events
//
// NOTE: To compare two experimental distributions with m and n events,
// use z = sqrt(m*n/(m+n))*dn
//
// Accuracy: The function is far too accurate for any imaginable application.
// Probabilities less than 10^-15 are returned as zero.
// However, remember that the formula is only valid for "large" n.
// Theta function inversion formula is used for z <= 1
//
// This function was translated by Rene Brun from PROBKL in CERNLIB
// cons[j] = -0.5*(PI*2*j-1)/2(**2
const Double_t cons[3] = { -1.233700550136 , -11.10330496 , -30.84251376};
// jf2[j] = -2* j**2
const Double_t fj2[5] = {-2. , -8. , -18. , -32. , -50.};
const Double_t sqr2pi = 2.50662827463;
Double_t p = 0;
Int_t j;
if (z < 0.2) return 1;
if (z > 1) { // use series in exp(z**2)
Double_t c;
Double_t sig2 = -2;
Double_t z2 = z*z;
for (j=0;j<5;j++) {
sig2 = -sig2;
c = fj2[j] *z2;
if (c < -100) return p;
p += sig2*TMath::Exp(c);
}
return p;
}
// z< 1 use series in exp(1/z**2)
Double_t zinv = 1/z;
Double_t a = sqr2pi*zinv;
Double_t zinv2 = zinv*zinv;
Double_t arg;
for (j=0;j<3;j++) {
arg = cons[j]*zinv2;
if (arg < -30) continue;
p += TMath::Exp(arg);
}
p = 1 - a*p;
return p;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TMath::LocMin(Int_t n, Short_t *a)
{
// Return index of array with the minimum element
// If more than one element is minimum returns first found
if (n <= 0) return -1;
Short_t xmin = a[0];
Int_t loc = 0;
for (Int_t i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (xmin > a[i]) {
xmin = a[i];
loc = i;
}
}
return loc;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TMath::LocMin(Int_t n, Int_t *a)
{
// Return index of array with the minimum element
// If more than one element is minimum returns first found
if (n <= 0) return -1;
Int_t xmin = a[0];
Int_t loc = 0;
for (Int_t i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (xmin > a[i]) {
xmin = a[i];
loc = i;
}
}
return loc;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TMath::LocMin(Int_t n, Float_t *a)
{
// Return index of array with the minimum element
// If more than one element is minimum returns first found
if (n <= 0) return -1;
Float_t xmin = a[0];
Int_t loc = 0;
for (Int_t i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (xmin > a[i]) {
xmin = a[i];
loc = i;
}
}
return loc;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TMath::LocMin(Int_t n, Double_t *a)
{
// Return index of array with the minimum element
// If more than one element is minimum returns first found
if (n <= 0) return -1;
Double_t xmin = a[0];
Int_t loc = 0;
for (Int_t i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (xmin > a[i]) {
xmin = a[i];
loc = i;
}
}
return loc;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TMath::LocMax(Int_t n, Short_t *a)
{
// Return index of array with the maximum element
// If more than one element is maximum returns first found
if (n <= 0) return -1;
Short_t xmax = a[0];
Int_t loc = 0;
for (Int_t i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (xmax < a[i]) {
xmax = a[i];
loc = i;
}
}
return loc;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TMath::LocMax(Int_t n, Int_t *a)
{
// Return index of array with the maximum element
// If more than one element is maximum returns first found
if (n <= 0) return -1;
Int_t xmax = a[0];
Int_t loc = 0;
for (Int_t i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (xmax < a[i]) {
xmax = a[i];
loc = i;
}
}
return loc;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TMath::LocMax(Int_t n, Float_t *a)
{
// Return index of array with the maximum element
// If more than one element is maximum returns first found
if (n <= 0) return -1;
Float_t xmax = a[0];
Int_t loc = 0;
for (Int_t i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (xmax < a[i]) {
xmax = a[i];
loc = i;
}
}
return loc;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TMath::LocMax(Int_t n, Double_t *a)
{
// Return index of array with the maximum element
// If more than one element is maximum returns first found
if (n <= 0) return -1;
Double_t xmax = a[0];
Int_t loc = 0;
for (Int_t i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (xmax < a[i]) {
xmax = a[i];
loc = i;
}
}
return loc;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TMath::BinarySearch(Int_t n, Short_t *array, Short_t value)
{
// Binary search in an array of n values to locate value
//
// Array is supposed to be sorted prior to this call.
// If match is found, function returns position of element.
// If no match found, function gives nearest element smaller than value.
Int_t nabove, nbelow, middle;
nabove = n+1;
nbelow = 0;
while(nabove-nbelow > 1) {
middle = (nabove+nbelow)/2;
if (value == array[middle-1]) return middle-1;
if (value < array[middle-1]) nabove = middle;
else nbelow = middle;
}
return nbelow-1;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TMath::BinarySearch(Int_t n, Short_t **array, Short_t value)
{
// Binary search in an array of n values to locate value
//
// Array is supposed to be sorted prior to this call.
// If match is found, function returns position of element.
// If no match found, function gives nearest element smaller than value.
Int_t nabove, nbelow, middle;
nabove = n+1;
nbelow = 0;
while(nabove-nbelow > 1) {
middle = (nabove+nbelow)/2;
if (value == *array[middle-1]) return middle-1;
if (value < *array[middle-1]) nabove = middle;
else nbelow = middle;
}
return nbelow-1;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TMath::BinarySearch(Int_t n, Int_t *array, Int_t value)
{
// Binary search in an array of n values to locate value
//
// Array is supposed to be sorted prior to this call.
// If match is found, function returns position of element.
// If no match found, function gives nearest element smaller than value.
Int_t nabove, nbelow, middle;
nabove = n+1;
nbelow = 0;
while(nabove-nbelow > 1) {
middle = (nabove+nbelow)/2;
if (value == array[middle-1]) return middle-1;
if (value < array[middle-1]) nabove = middle;
else nbelow = middle;
}
return nbelow-1;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TMath::BinarySearch(Int_t n, Int_t **array, Int_t value)
{
// Binary search in an array of n values to locate value
//
// Array is supposed to be sorted prior to this call.
// If match is found, function returns position of element.
// If no match found, function gives nearest element smaller than value.
Int_t nabove, nbelow, middle;
nabove = n+1;
nbelow = 0;
while(nabove-nbelow > 1) {
middle = (nabove+nbelow)/2;
if (value == *array[middle-1]) return middle-1;
if (value < *array[middle-1]) nabove = middle;
else nbelow = middle;
}
return nbelow-1;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TMath::BinarySearch(Int_t n, Float_t *array, Float_t value)
{
// Binary search in an array of n values to locate value
//
// Array is supposed to be sorted prior to this call.
// If match is found, function returns position of element.
// If no match found, function gives nearest element smaller than value.
Int_t nabove, nbelow, middle;
nabove = n+1;
nbelow = 0;
while(nabove-nbelow > 1) {
middle = (nabove+nbelow)/2;
if (value == array[middle-1]) return middle-1;
if (value < array[middle-1]) nabove = middle;
else nbelow = middle;
}
return nbelow-1;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TMath::BinarySearch(Int_t n, Float_t **array, Float_t value)
{
// Binary search in an array of n values to locate value
//
// Array is supposed to be sorted prior to this call.
// If match is found, function returns position of element.
// If no match found, function gives nearest element smaller than value.
Int_t nabove, nbelow, middle;
nabove = n+1;
nbelow = 0;
while(nabove-nbelow > 1) {
middle = (nabove+nbelow)/2;
if (value == *array[middle-1]) return middle-1;
if (value < *array[middle-1]) nabove = middle;
else nbelow = middle;
}
return nbelow-1;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TMath::BinarySearch(Int_t n, Double_t *array, Double_t value)
{
// Binary search in an array of n values to locate value
//
// Array is supposed to be sorted prior to this call.
// If match is found, function returns position of element.
// If no match found, function gives nearest element smaller than value.
Int_t nabove, nbelow, middle;
nabove = n+1;
nbelow = 0;
while(nabove-nbelow > 1) {
middle = (nabove+nbelow)/2;
if (value == array[middle-1]) return middle-1;
if (value < array[middle-1]) nabove = middle;
else nbelow = middle;
}
return nbelow-1;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TMath::BinarySearch(Int_t n, Double_t **array, Double_t value)
{
// Binary search in an array of n values to locate value
//
// Array is supposed to be sorted prior to this call.
// If match is found, function returns position of element.
// If no match found, function gives nearest element smaller than value.
Int_t nabove, nbelow, middle;
nabove = n+1;
nbelow = 0;
while(nabove-nbelow > 1) {
middle = (nabove+nbelow)/2;
if (value == *array[middle-1]) return middle-1;
if (value < *array[middle-1]) nabove = middle;
else nbelow = middle;
}
return nbelow-1;
}
//_____________________________________________________________________________
void TMath::Sort(Int_t n1, Short_t *a, Int_t *index, Bool_t down)
{
// Sort the n1 elements of the Short_t array a.
// In output the array index contains the indices of the sorted array.
// If down is false sort in increasing order (default is decreasing order).
// This is a translation of the CERNLIB routine sortzv (M101)
// based on the quicksort algorithm.
// NOTE that the array index must be created with a length >= n1
// before calling this function.
Int_t i,i1,n,i2,i3,i33,i222,iswap,n2;
Int_t i22 = 0;
Short_t ai;
n = n1;
if (n <= 0) return;
if (n == 1) {index[0] = 0; return;}
for (i=0;i<n;i++) index[i] = i+1;
for (i1=2;i1<=n;i1++) {
i3 = i1;
i33 = index[i3-1];
ai = a[i33-1];
while(1) {
i2 = i3/2;
if (i2 <= 0) break;
i22 = index[i2-1];
if (ai <= a[i22-1]) break;
index[i3-1] = i22;
i3 = i2;
}
index[i3-1] = i33;
}
while(1) {
i3 = index[n-1];
index[n-1] = index[0];
ai = a[i3-1];
n--;
if(n-1 < 0) {index[0] = i3; break;}
i1 = 1;
while(2) {
i2 = i1+i1;
if (i2 <= n) i22 = index[i2-1];
if (i2-n > 0) {index[i1-1] = i3; break;}
if (i2-n < 0) {
i222 = index[i2];
if (a[i22-1] - a[i222-1] < 0) {
i2++;
i22 = i222;
}
}
if (ai - a[i22-1] > 0) {index[i1-1] = i3; break;}
index[i1-1] = i22;
i1 = i2;
}
}
for (i=0;i<n1;i++) index[i]--;
if (!down) return;
n2 = n1/2;
for (i=0;i<n2;i++) {
iswap = index[i];
index[i] = index[n1-i-1];
index[n1-i-1] = iswap;
}
}
//_____________________________________________________________________________
void TMath::Sort(Int_t n1, Int_t *a, Int_t *index, Bool_t down)
{
// Sort the n1 elements of the Int_t array a.
// In output the array index contains the indices of the sorted array.
// If down is false sort in increasing order (default is decreasing order).
// This is a translation of the CERNLIB routine sortzv (M101)
// based on the quicksort algorithm.
// NOTE that the array index must be created with a length >= n1
// before calling this function.
Int_t i,i1,n,i2,i3,i33,i222,iswap,n2;
Int_t i22 = 0;
Int_t ai;
n = n1;
if (n <= 0) return;
if (n == 1) {index[0] = 0; return;}
for (i=0;i<n;i++) index[i] = i+1;
for (i1=2;i1<=n;i1++) {
i3 = i1;
i33 = index[i3-1];
ai = a[i33-1];
while(1) {
i2 = i3/2;
if (i2 <= 0) break;
i22 = index[i2-1];
if (ai <= a[i22-1]) break;
index[i3-1] = i22;
i3 = i2;
}
index[i3-1] = i33;
}
while(1) {
i3 = index[n-1];
index[n-1] = index[0];
ai = a[i3-1];
n--;
if(n-1 < 0) {index[0] = i3; break;}
i1 = 1;
while(2) {
i2 = i1+i1;
if (i2 <= n) i22 = index[i2-1];
if (i2-n > 0) {index[i1-1] = i3; break;}
if (i2-n < 0) {
i222 = index[i2];
if (a[i22-1] - a[i222-1] < 0) {
i2++;
i22 = i222;
}
}
if (ai - a[i22-1] > 0) {index[i1-1] = i3; break;}
index[i1-1] = i22;
i1 = i2;
}
}
for (i=0;i<n1;i++) index[i]--;
if (!down) return;
n2 = n1/2;
for (i=0;i<n2;i++) {
iswap = index[i];
index[i] = index[n1-i-1];
index[n1-i-1] = iswap;
}
}
//_____________________________________________________________________________
void TMath::Sort(Int_t n1, Float_t *a, Int_t *index, Bool_t down)
{
// Sort the n1 elements of the Float_t array a.
// In output the array index contains the indices of the sorted array.
// If down is false sort in increasing order (default is decreasing order).
// This is a translation of the CERNLIB routine sortzv (M101)
// based on the quicksort algorithm.
// NOTE that the array index must be created with a length >= n1
// before calling this function.
Int_t i,i1,n,i2,i3,i33,i222,iswap,n2;
Int_t i22 = 0;
Float_t ai;
n = n1;
if (n <= 0) return;
if (n == 1) {index[0] = 0; return;}
for (i=0;i<n;i++) index[i] = i+1;
for (i1=2;i1<=n;i1++) {
i3 = i1;
i33 = index[i3-1];
ai = a[i33-1];
while(1) {
i2 = i3/2;
if (i2 <= 0) break;
i22 = index[i2-1];
if (ai <= a[i22-1]) break;
index[i3-1] = i22;
i3 = i2;
}
index[i3-1] = i33;
}
while(1) {
i3 = index[n-1];
index[n-1] = index[0];
ai = a[i3-1];
n--;
if(n-1 < 0) {index[0] = i3; break;}
i1 = 1;
while(2) {
i2 = i1+i1;
if (i2 <= n) i22 = index[i2-1];
if (i2-n > 0) {index[i1-1] = i3; break;}
if (i2-n < 0) {
i222 = index[i2];
if (a[i22-1] - a[i222-1] < 0) {
i2++;
i22 = i222;
}
}
if (ai - a[i22-1] > 0) {index[i1-1] = i3; break;}
index[i1-1] = i22;
i1 = i2;
}
}
for (i=0;i<n1;i++) index[i]--;
if (!down) return;
n2 = n1/2;
for (i=0;i<n2;i++) {
iswap = index[i];
index[i] = index[n1-i-1];
index[n1-i-1] = iswap;
}
}
//_____________________________________________________________________________
void TMath::Sort(Int_t n1, Double_t *a, Int_t *index, Bool_t down)
{
// Sort the n1 elements of the Double_t array a.
// In output the array index contains the indices of the sorted array.
// If down is false sort in increasing order (default is decreasing order).
// This is a translation of the CERNLIB routine sortzv (M101)
// based on the quicksort algorithm.
// NOTE that the array index must be created with a length >= n1
// before calling this function.
Int_t i,i1,n,i2,i3,i33,i222,iswap,n2;
Int_t i22 = 0;
Double_t ai;
n = n1;
if (n <= 0) return;
if (n == 1) {index[0] = 0; return;}
for (i=0;i<n;i++) index[i] = i+1;
for (i1=2;i1<=n;i1++) {
i3 = i1;
i33 = index[i3-1];
ai = a[i33-1];
while(1) {
i2 = i3/2;
if (i2 <= 0) break;
i22 = index[i2-1];
if (ai <= a[i22-1]) break;
index[i3-1] = i22;
i3 = i2;
}
index[i3-1] = i33;
}
while(1) {
i3 = index[n-1];
index[n-1] = index[0];
ai = a[i3-1];
n--;
if(n-1 < 0) {index[0] = i3; break;}
i1 = 1;
while(2) {
i2 = i1+i1;
if (i2 <= n) i22 = index[i2-1];
if (i2-n > 0) {index[i1-1] = i3; break;}
if (i2-n < 0) {
i222 = index[i2];
if (a[i22-1] - a[i222-1] < 0) {
i2++;
i22 = i222;
}
}
if (ai - a[i22-1] > 0) {index[i1-1] = i3; break;}
index[i1-1] = i22;
i1 = i2;
}
}
for (i=0;i<n1;i++) index[i]--;
if (!down) return;
n2 = n1/2;
for (i=0;i<n2;i++) {
iswap = index[i];
index[i] = index[n1-i-1];
index[n1-i-1] = iswap;
}
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
ULong_t TMath::Hash(const void *txt, Int_t ntxt)
{
// Calculates hash index from any char string
// based on precalculated table of 256 specially selected
// random numbers.
//
// For string: i = TExMap::Hash(string,nstring);
// For int: i = TExMap::Hash(&intword,sizeof(int));
// For pointer: i = TExMap::Hash(&pointer,sizeof(void*));
//
// Limitation: for ntxt>256 calculates hash only from first 256 bytes
//
// V.Perev
const UChar_t *uc = (const UChar_t*) txt;
ULong_t u = 0, uu = 0;
static ULong_t utab[256] =
{0xb93f6fc0,0x553dfc51,0xb22c1e8c,0x638462c0,0x13e81418,0x2836e171,0x7c4abb90,0xda1a4f39
,0x38f211d1,0x8c804829,0x95a6602d,0x4c590993,0x1810580a,0x721057d4,0x0f587215,0x9f49ce2a
,0xcd5ab255,0xab923a99,0x80890f39,0xbcfa2290,0x16587b52,0x6b6d3f0d,0xea8ff307,0x51542d5c
,0x189bf223,0x39643037,0x0e4a326a,0x214eca01,0x47645a9b,0x0f364260,0x8e9b2da4,0x5563ebd9
,0x57a31c1c,0xab365854,0xdd63ab1f,0x0b89acbd,0x23d57d33,0x1800a0fd,0x225ac60a,0xd0e51943
,0x6c65f669,0xcb966ea0,0xcbafda95,0x2e5c0c5f,0x2988e87e,0xc781cbab,0x3add3dc7,0x693a2c30
,0x42d6c23c,0xebf85f26,0x2544987e,0x2e315e3f,0xac88b5b5,0x7ebd2bbb,0xda07c87b,0x20d460f1
,0xc61c3f40,0x182046e7,0x3b6c3b66,0x2fc10d4a,0x0780dfbb,0xc437280c,0x0988dd07,0xe1498606
,0x8e61d728,0x4f1f3909,0x040a9682,0x49411b29,0x391b0e1c,0xd7905241,0xdd77d95b,0x88426c13
,0x33033e58,0xe158e30e,0x7e342647,0x1e09544b,0x4637353d,0x18ea0924,0x39212b08,0x12580ae8
,0x269a6f06,0x3e10b73b,0x123db33b,0x085412da,0x3bb5f464,0xd9b2d442,0x103d26bb,0xd0038bab
,0x45b6177f,0xfb48f1fe,0x99074c55,0xb545e82e,0x5f79fd0d,0x570f3ae4,0x57e43255,0x037a12ae
,0x4357bdb2,0x337c2c4d,0x2982499d,0x2ab72793,0x3900e7d1,0x57a6bb81,0x7503609b,0x3f39c0d0
,0x717b389d,0x5748034f,0x4698162b,0x5801b97c,0x1dfd5d7e,0xc1386d1c,0xa387a72a,0x084547e4
,0x2e54d8e9,0x2e2f384c,0xe09ccc20,0x8904b71e,0x3e24edc5,0x06a22e16,0x8a2be1df,0x9e5058b2
,0xe01a2f16,0x03325eed,0x587ecfe6,0x584d9cd3,0x32926930,0xe943d68c,0xa9442da8,0xf9650560
,0xf003871e,0x1109c663,0x7a2f2f89,0x1c2210bb,0x37335787,0xb92b382f,0xea605cb5,0x336bbe38
,0x08126bd3,0x1f8c2bd6,0xba6c46f2,0x1a4d1b83,0xc988180d,0xe2582505,0xa8a1b375,0x59a08c49
,0x3db54b48,0x44400f35,0x272d4e7f,0x5579f733,0x98eb590e,0x8ee09813,0x12cc9301,0xc85c402d
,0x135c1039,0x22318128,0x4063c705,0x87a8a3fa,0xfc14431f,0x6e27bf47,0x2d080a19,0x01dba174
,0xe343530b,0xaa1bfced,0x283bb2c8,0x5df250c8,0x4ff9140b,0x045039c1,0xa377780d,0x750f2661
,0x2b108918,0x0b152120,0x3cbc251f,0x5e87b350,0x060625bb,0xe068ba3b,0xdb73ebd7,0x66014ff3
,0xdb003000,0x161a3a0b,0xdc24e142,0x97ea5575,0x635a3cab,0xa719100a,0x256084db,0xc1f4a1e7
,0xe13388f2,0xb8199fc9,0x50c70dc9,0x08154211,0xd60e5220,0xe52c6592,0x584c5fe1,0xfe5e0875
,0x21072b30,0x3370d773,0x92608fe2,0x2d013d93,0x53414b3c,0x2c066142,0x64676644,0x0420887c
,0x35c01187,0x6822119b,0xf9bfe6df,0x273f4ee4,0x87973149,0x7b41282d,0x635d0d1f,0x5f7ecc1e
,0x14c3608a,0x462dfdab,0xc33d8808,0x1dcd995e,0x0fcb11ba,0x11755914,0x5a62044b,0x37f76755
,0x345bd058,0x8831c2b5,0x204a8468,0x3b0b1cd2,0x444e56f4,0x97a93e2c,0xd5f15067,0x266a95fa
,0xff4f8036,0x6160060d,0x930c472f,0xed922184,0x37120251,0xc0add74f,0x1c0bc89d,0x018d47f2
,0xff59ef66,0xd1901a17,0x91f6701b,0x0960082f,0x86f6a8f3,0x1154fecd,0x9867d1de,0x0945482f
,0x790ffcac,0xe5610011,0x4765637e,0xa745dbff,0x841fdcb3,0x4f7372a0,0x3c05013d,0xf1ac4ab7
,0x3bc5b5cc,0x49a73349,0x356a7f67,0x1174f031,0x11d32634,0x4413d301,0x1dd285c4,0x3fae4800
};
ntxt &= 255;
for ( ; ntxt--; uc++) {
uu = uu<<1 ^ utab[(*uc) ^ ntxt];
u ^= uu;
}
return u;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
ULong_t TMath::Hash(const char *txt)
{
return Hash(txt, Int_t(strlen(txt)));
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::BesselI0(Double_t x)
{
// Computation of the modified Bessel function I_0(x) for any real x.
//
// The algorithm is based on the article by Abramowitz and Stegun [1]
// as denoted in Numerical Recipes 2nd ed. on p. 230 (W.H.Press et al.).
//
// [1] M.Abramowitz and I.A.Stegun, Handbook of Mathematical Functions,
// Applied Mathematics Series vol. 55 (1964), Washington.
//
//--- NvE 12-mar-2000 UU-SAP Utrecht
// Parameters of the polynomial approximation
const Double_t p1=1.0, p2=3.5156229, p3=3.0899424,
p4=1.2067492, p5=0.2659732, p6=3.60768e-2, p7=4.5813e-3;
const Double_t q1= 0.39894228, q2= 1.328592e-2, q3= 2.25319e-3,
q4=-1.57565e-3, q5= 9.16281e-3, q6=-2.057706e-2,
q7= 2.635537e-2, q8=-1.647633e-2, q9= 3.92377e-3;
Double_t ax = TMath::Abs(x);
Double_t y=0, result=0;
if (ax < 3.75) {
y = pow(x/3.75,2);
result = p1+y*(p2+y*(p3+y*(p4+y*(p5+y*(p6+y*p7)))));
} else {
y = 3.75/ax;
result = (exp(ax)/sqrt(ax))*(q1+y*(q2+y*(q3+y*(q4+y*(q5+y*(q6+y*(q7+y*(q8+y*q9))))))));
}
return result;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::BesselK0(Double_t x)
{
// Computation of the modified Bessel function K_0(x) for positive real x.
//
// The algorithm is based on the article by Abramowitz and Stegun [1]
// as denoted in Numerical Recipes 2nd ed. on p. 230 (W.H.Press et al.).
//
// [1] M.Abramowitz and I.A.Stegun, Handbook of Mathematical Functions,
// Applied Mathematics Series vol. 55 (1964), Washington.
//
//--- NvE 12-mar-2000 UU-SAP Utrecht
// Parameters of the polynomial approximation
const Double_t p1=-0.57721566, p2=0.42278420, p3=0.23069756,
p4= 3.488590e-2, p5=2.62698e-3, p6=1.0750e-4, p7=7.4e-5;
const Double_t q1= 1.25331414, q2=-7.832358e-2, q3= 2.189568e-2,
q4=-1.062446e-2, q5= 5.87872e-3, q6=-2.51540e-3, q7=5.3208e-4;
if (x <= 0) {
printf(" *K0* Invalid argument x = %gn",x);
return 0;
}
Double_t y=0,result=0;
if (x <= 2) {
y = x*x/4.;
result = (-log(x/2.)*TMath::BesselI0(x))+(p1+y*(p2+y*(p3+y*(p4+y*(p5+y*(p6+y*p7))))));
} else {
y = 2./x;
result = (exp(-x)/sqrt(x))*(q1+y*(q2+y*(q3+y*(q4+y*(q5+y*(q6+y*q7))))));
}
return result;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::BesselI1(Double_t x)
{
// Computation of the modified Bessel function I_1(x) for any real x.
//
// The algorithm is based on the article by Abramowitz and Stegun [1]
// as denoted in Numerical Recipes 2nd ed. on p. 230 (W.H.Press et al.).
//
// [1] M.Abramowitz and I.A.Stegun, Handbook of Mathematical Functions,
// Applied Mathematics Series vol. 55 (1964), Washington.
//
//--- NvE 12-mar-2000 UU-SAP Utrecht
// Parameters of the polynomial approximation
const Double_t p1=0.5, p2=0.87890594, p3=0.51498869,
p4=0.15084934, p5=2.658733e-2, p6=3.01532e-3, p7=3.2411e-4;
const Double_t q1= 0.39894228, q2=-3.988024e-2, q3=-3.62018e-3,
q4= 1.63801e-3, q5=-1.031555e-2, q6= 2.282967e-2,
q7=-2.895312e-2, q8= 1.787654e-2, q9=-4.20059e-3;
Double_t ax = TMath::Abs(x);
Double_t y=0, result=0;
if (ax < 3.75) {
y = pow(x/3.75,2);
result = x*(p1+y*(p2+y*(p3+y*(p4+y*(p5+y*(p6+y*p7))))));
} else {
y = 3.75/ax;
result = (exp(ax)/sqrt(ax))*(q1+y*(q2+y*(q3+y*(q4+y*(q5+y*(q6+y*(q7+y*(q8+y*q9))))))));
if (x < 0) result = -result;
}
return result;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::BesselK1(Double_t x)
{
// Computation of the modified Bessel function K_1(x) for positive real x.
//
// The algorithm is based on the article by Abramowitz and Stegun [1]
// as denoted in Numerical Recipes 2nd ed. on p. 230 (W.H.Press et al.).
//
// [1] M.Abramowitz and I.A.Stegun, Handbook of Mathematical Functions,
// Applied Mathematics Series vol. 55 (1964), Washington.
//
//--- NvE 12-mar-2000 UU-SAP Utrecht
// Parameters of the polynomial approximation
const Double_t p1= 1., p2= 0.15443144, p3=-0.67278579,
p4=-0.18156897, p5=-1.919402e-2, p6=-1.10404e-3, p7=-4.686e-5;
const Double_t q1= 1.25331414, q2= 0.23498619, q3=-3.655620e-2,
q4= 1.504268e-2, q5=-7.80353e-3, q6= 3.25614e-3, q7=-6.8245e-4;
if (x <= 0) {
printf(" *K1* Invalid argument x = %gn",x);
return 0;
}
Double_t y=0,result=0;
if (x <= 2) {
y = x*x/4.;
result = (log(x/2.)*TMath::BesselI1(x))+(1./x)*(p1+y*(p2+y*(p3+y*(p4+y*(p5+y*(p6+y*p7))))));
} else {
y = 2./x;
result = (exp(-x)/sqrt(x))*(q1+y*(q2+y*(q3+y*(q4+y*(q5+y*(q6+y*q7))))));
}
return result;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::BesselK(Int_t n,Double_t x)
{
// Computation of the Integer Order Modified Bessel function K_n(x)
// for n=0,1,2,... and positive real x.
//
// The algorithm uses the recurrence relation
//
// K_n+1(x) = (2n/x)*K_n(x) + K_n-1(x)
//
// as denoted in Numerical Recipes 2nd ed. on p. 232 (W.H.Press et al.).
//
//--- NvE 12-mar-2000 UU-SAP Utrecht
if (x <= 0 || n < 0) {
printf(" *K* Invalid argument(s) (n,x) = (%d, %g)n",n,x);
return 0;
}
if (n==0) return TMath::BesselK0(x);
if (n==1) return TMath::BesselK1(x);
// Perform upward recurrence for all x
Double_t tox = 2./x;
Double_t bkm = TMath::BesselK0(x);
Double_t bk = TMath::BesselK1(x);
Double_t bkp = 0;
for (Int_t j=1; j<n; j++) {
bkp = bkm+Double_t(j)*tox*bk;
bkm = bk;
bk = bkp;
}
return bk;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::BesselI(Int_t n,Double_t x)
{
// Computation of the Integer Order Modified Bessel function I_n(x)
// for n=0,1,2,... and any real x.
//
// The algorithm uses the recurrence relation
//
// I_n+1(x) = (-2n/x)*I_n(x) + I_n-1(x)
//
// as denoted in Numerical Recipes 2nd ed. on p. 232 (W.H.Press et al.).
//
//--- NvE 12-mar-2000 UU-SAP Utrecht
Int_t iacc = 40; // Increase to enhance accuracy
Double_t bigno = 1.e10, bigni = 1.e-10;
if (n < 0) {
printf(" *I* Invalid argument (n,x) = (%d, %g)n",n,x);
return 0;
}
if (n==0) return TMath::BesselI0(x);
if (n==1) return TMath::BesselI1(x);
if (TMath::Abs(x) < 1.e-10) return 0;
Double_t tox = 2./TMath::Abs(x);
Double_t bip = 0,bim = 0;
Double_t bi = 1;
Double_t result = 0;
Int_t m = 2*((n+Int_t(sqrt(Float_t(iacc*n))))); // Downward recurrence from even m
for (Int_t j=m; j<=1; j--) {
bim = bip+Double_t(j)*tox*bi;
bip = bi;
bi = bim;
// Renormalise to prevent overflows
if (TMath::Abs(bi) > bigno) {
result *= bigni;
bi *= bigni;
bip *= bigni;
}
if (j==n) result=bip;
}
result *= TMath::BesselI0(x)/bi; // Normalise with BesselI0(x)
if ((x < 0) && (n%2 == 1)) result = -result;
return result;
}
*/
//
// which gives the probability that Kolmogorov's test statistic will exceed
// the value z assuming the null hypothesis. This gives a very powerful
// test for comparing two one-dimensional distributions.
// see, for example, Eadie et al, "statistocal Methods in Experimental
// Physics', pp 269-270).
//
// This function returns the confidence level for the null hypothesis, where:
// z = dn*sqrt(n), and
// dn is the maximum deviation between a hypothetical distribution
// function and an experimental distribution with
// n events
//
// NOTE: To compare two experimental distributions with m and n events,
// use z = sqrt(m*n/(m+n))*dn
//
// Accuracy: The function is far too accurate for any imaginable application.
// Probabilities less than 10^-15 are returned as zero.
// However, remember that the formula is only valid for "large" n.
// Theta function inversion formula is used for z <= 1
//
// This function was translated by Rene Brun from PROBKL in CERNLIB
// cons[j] = -0.5*(PI*2*j-1)/2(**2
const Double_t cons[3] = { -1.233700550136 , -11.10330496 , -30.84251376};
// jf2[j] = -2* j**2
const Double_t fj2[5] = {-2. , -8. , -18. , -32. , -50.};
const Double_t sqr2pi = 2.50662827463;
Double_t p = 0;
Int_t j;
if (z < 0.2) return 1;
if (z > 1) { // use series in exp(z**2)
Double_t c;
Double_t sig2 = -2;
Double_t z2 = z*z;
for (j=0;j<5;j++) {
sig2 = -sig2;
c = fj2[j] *z2;
if (c < -100) return p;
p += sig2*TMath::Exp(c);
}
return p;
}
// z< 1 use series in exp(1/z**2)
Double_t zinv = 1/z;
Double_t a = sqr2pi*zinv;
Double_t zinv2 = zinv*zinv;
Double_t arg;
for (j=0;j<3;j++) {
arg = cons[j]*zinv2;
if (arg < -30) continue;
p += TMath::Exp(arg);
}
p = 1 - a*p;
return p;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TMath::LocMin(Int_t n, Short_t *a)
{
// Return index of array with the minimum element
// If more than one element is minimum returns first found
if (n <= 0) return -1;
Short_t xmin = a[0];
Int_t loc = 0;
for (Int_t i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (xmin > a[i]) {
xmin = a[i];
loc = i;
}
}
return loc;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TMath::LocMin(Int_t n, Int_t *a)
{
// Return index of array with the minimum element
// If more than one element is minimum returns first found
if (n <= 0) return -1;
Int_t xmin = a[0];
Int_t loc = 0;
for (Int_t i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (xmin > a[i]) {
xmin = a[i];
loc = i;
}
}
return loc;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TMath::LocMin(Int_t n, Float_t *a)
{
// Return index of array with the minimum element
// If more than one element is minimum returns first found
if (n <= 0) return -1;
Float_t xmin = a[0];
Int_t loc = 0;
for (Int_t i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (xmin > a[i]) {
xmin = a[i];
loc = i;
}
}
return loc;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TMath::LocMin(Int_t n, Double_t *a)
{
// Return index of array with the minimum element
// If more than one element is minimum returns first found
if (n <= 0) return -1;
Double_t xmin = a[0];
Int_t loc = 0;
for (Int_t i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (xmin > a[i]) {
xmin = a[i];
loc = i;
}
}
return loc;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TMath::LocMax(Int_t n, Short_t *a)
{
// Return index of array with the maximum element
// If more than one element is maximum returns first found
if (n <= 0) return -1;
Short_t xmax = a[0];
Int_t loc = 0;
for (Int_t i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (xmax < a[i]) {
xmax = a[i];
loc = i;
}
}
return loc;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TMath::LocMax(Int_t n, Int_t *a)
{
// Return index of array with the maximum element
// If more than one element is maximum returns first found
if (n <= 0) return -1;
Int_t xmax = a[0];
Int_t loc = 0;
for (Int_t i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (xmax < a[i]) {
xmax = a[i];
loc = i;
}
}
return loc;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TMath::LocMax(Int_t n, Float_t *a)
{
// Return index of array with the maximum element
// If more than one element is maximum returns first found
if (n <= 0) return -1;
Float_t xmax = a[0];
Int_t loc = 0;
for (Int_t i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (xmax < a[i]) {
xmax = a[i];
loc = i;
}
}
return loc;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TMath::LocMax(Int_t n, Double_t *a)
{
// Return index of array with the maximum element
// If more than one element is maximum returns first found
if (n <= 0) return -1;
Double_t xmax = a[0];
Int_t loc = 0;
for (Int_t i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (xmax < a[i]) {
xmax = a[i];
loc = i;
}
}
return loc;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TMath::BinarySearch(Int_t n, Short_t *array, Short_t value)
{
// Binary search in an array of n values to locate value
//
// Array is supposed to be sorted prior to this call.
// If match is found, function returns position of element.
// If no match found, function gives nearest element smaller than value.
Int_t nabove, nbelow, middle;
nabove = n+1;
nbelow = 0;
while(nabove-nbelow > 1) {
middle = (nabove+nbelow)/2;
if (value == array[middle-1]) return middle-1;
if (value < array[middle-1]) nabove = middle;
else nbelow = middle;
}
return nbelow-1;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TMath::BinarySearch(Int_t n, Short_t **array, Short_t value)
{
// Binary search in an array of n values to locate value
//
// Array is supposed to be sorted prior to this call.
// If match is found, function returns position of element.
// If no match found, function gives nearest element smaller than value.
Int_t nabove, nbelow, middle;
nabove = n+1;
nbelow = 0;
while(nabove-nbelow > 1) {
middle = (nabove+nbelow)/2;
if (value == *array[middle-1]) return middle-1;
if (value < *array[middle-1]) nabove = middle;
else nbelow = middle;
}
return nbelow-1;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TMath::BinarySearch(Int_t n, Int_t *array, Int_t value)
{
// Binary search in an array of n values to locate value
//
// Array is supposed to be sorted prior to this call.
// If match is found, function returns position of element.
// If no match found, function gives nearest element smaller than value.
Int_t nabove, nbelow, middle;
nabove = n+1;
nbelow = 0;
while(nabove-nbelow > 1) {
middle = (nabove+nbelow)/2;
if (value == array[middle-1]) return middle-1;
if (value < array[middle-1]) nabove = middle;
else nbelow = middle;
}
return nbelow-1;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TMath::BinarySearch(Int_t n, Int_t **array, Int_t value)
{
// Binary search in an array of n values to locate value
//
// Array is supposed to be sorted prior to this call.
// If match is found, function returns position of element.
// If no match found, function gives nearest element smaller than value.
Int_t nabove, nbelow, middle;
nabove = n+1;
nbelow = 0;
while(nabove-nbelow > 1) {
middle = (nabove+nbelow)/2;
if (value == *array[middle-1]) return middle-1;
if (value < *array[middle-1]) nabove = middle;
else nbelow = middle;
}
return nbelow-1;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TMath::BinarySearch(Int_t n, Float_t *array, Float_t value)
{
// Binary search in an array of n values to locate value
//
// Array is supposed to be sorted prior to this call.
// If match is found, function returns position of element.
// If no match found, function gives nearest element smaller than value.
Int_t nabove, nbelow, middle;
nabove = n+1;
nbelow = 0;
while(nabove-nbelow > 1) {
middle = (nabove+nbelow)/2;
if (value == array[middle-1]) return middle-1;
if (value < array[middle-1]) nabove = middle;
else nbelow = middle;
}
return nbelow-1;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TMath::BinarySearch(Int_t n, Float_t **array, Float_t value)
{
// Binary search in an array of n values to locate value
//
// Array is supposed to be sorted prior to this call.
// If match is found, function returns position of element.
// If no match found, function gives nearest element smaller than value.
Int_t nabove, nbelow, middle;
nabove = n+1;
nbelow = 0;
while(nabove-nbelow > 1) {
middle = (nabove+nbelow)/2;
if (value == *array[middle-1]) return middle-1;
if (value < *array[middle-1]) nabove = middle;
else nbelow = middle;
}
return nbelow-1;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TMath::BinarySearch(Int_t n, Double_t *array, Double_t value)
{
// Binary search in an array of n values to locate value
//
// Array is supposed to be sorted prior to this call.
// If match is found, function returns position of element.
// If no match found, function gives nearest element smaller than value.
Int_t nabove, nbelow, middle;
nabove = n+1;
nbelow = 0;
while(nabove-nbelow > 1) {
middle = (nabove+nbelow)/2;
if (value == array[middle-1]) return middle-1;
if (value < array[middle-1]) nabove = middle;
else nbelow = middle;
}
return nbelow-1;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TMath::BinarySearch(Int_t n, Double_t **array, Double_t value)
{
// Binary search in an array of n values to locate value
//
// Array is supposed to be sorted prior to this call.
// If match is found, function returns position of element.
// If no match found, function gives nearest element smaller than value.
Int_t nabove, nbelow, middle;
nabove = n+1;
nbelow = 0;
while(nabove-nbelow > 1) {
middle = (nabove+nbelow)/2;
if (value == *array[middle-1]) return middle-1;
if (value < *array[middle-1]) nabove = middle;
else nbelow = middle;
}
return nbelow-1;
}
//_____________________________________________________________________________
void TMath::Sort(Int_t n1, Short_t *a, Int_t *index, Bool_t down)
{
// Sort the n1 elements of the Short_t array a.
// In output the array index contains the indices of the sorted array.
// If down is false sort in increasing order (default is decreasing order).
// This is a translation of the CERNLIB routine sortzv (M101)
// based on the quicksort algorithm.
// NOTE that the array index must be created with a length >= n1
// before calling this function.
Int_t i,i1,n,i2,i3,i33,i222,iswap,n2;
Int_t i22 = 0;
Short_t ai;
n = n1;
if (n <= 0) return;
if (n == 1) {index[0] = 0; return;}
for (i=0;i<n;i++) index[i] = i+1;
for (i1=2;i1<=n;i1++) {
i3 = i1;
i33 = index[i3-1];
ai = a[i33-1];
while(1) {
i2 = i3/2;
if (i2 <= 0) break;
i22 = index[i2-1];
if (ai <= a[i22-1]) break;
index[i3-1] = i22;
i3 = i2;
}
index[i3-1] = i33;
}
while(1) {
i3 = index[n-1];
index[n-1] = index[0];
ai = a[i3-1];
n--;
if(n-1 < 0) {index[0] = i3; break;}
i1 = 1;
while(2) {
i2 = i1+i1;
if (i2 <= n) i22 = index[i2-1];
if (i2-n > 0) {index[i1-1] = i3; break;}
if (i2-n < 0) {
i222 = index[i2];
if (a[i22-1] - a[i222-1] < 0) {
i2++;
i22 = i222;
}
}
if (ai - a[i22-1] > 0) {index[i1-1] = i3; break;}
index[i1-1] = i22;
i1 = i2;
}
}
for (i=0;i<n1;i++) index[i]--;
if (!down) return;
n2 = n1/2;
for (i=0;i<n2;i++) {
iswap = index[i];
index[i] = index[n1-i-1];
index[n1-i-1] = iswap;
}
}
//_____________________________________________________________________________
void TMath::Sort(Int_t n1, Int_t *a, Int_t *index, Bool_t down)
{
// Sort the n1 elements of the Int_t array a.
// In output the array index contains the indices of the sorted array.
// If down is false sort in increasing order (default is decreasing order).
// This is a translation of the CERNLIB routine sortzv (M101)
// based on the quicksort algorithm.
// NOTE that the array index must be created with a length >= n1
// before calling this function.
Int_t i,i1,n,i2,i3,i33,i222,iswap,n2;
Int_t i22 = 0;
Int_t ai;
n = n1;
if (n <= 0) return;
if (n == 1) {index[0] = 0; return;}
for (i=0;i<n;i++) index[i] = i+1;
for (i1=2;i1<=n;i1++) {
i3 = i1;
i33 = index[i3-1];
ai = a[i33-1];
while(1) {
i2 = i3/2;
if (i2 <= 0) break;
i22 = index[i2-1];
if (ai <= a[i22-1]) break;
index[i3-1] = i22;
i3 = i2;
}
index[i3-1] = i33;
}
while(1) {
i3 = index[n-1];
index[n-1] = index[0];
ai = a[i3-1];
n--;
if(n-1 < 0) {index[0] = i3; break;}
i1 = 1;
while(2) {
i2 = i1+i1;
if (i2 <= n) i22 = index[i2-1];
if (i2-n > 0) {index[i1-1] = i3; break;}
if (i2-n < 0) {
i222 = index[i2];
if (a[i22-1] - a[i222-1] < 0) {
i2++;
i22 = i222;
}
}
if (ai - a[i22-1] > 0) {index[i1-1] = i3; break;}
index[i1-1] = i22;
i1 = i2;
}
}
for (i=0;i<n1;i++) index[i]--;
if (!down) return;
n2 = n1/2;
for (i=0;i<n2;i++) {
iswap = index[i];
index[i] = index[n1-i-1];
index[n1-i-1] = iswap;
}
}
//_____________________________________________________________________________
void TMath::Sort(Int_t n1, Float_t *a, Int_t *index, Bool_t down)
{
// Sort the n1 elements of the Float_t array a.
// In output the array index contains the indices of the sorted array.
// If down is false sort in increasing order (default is decreasing order).
// This is a translation of the CERNLIB routine sortzv (M101)
// based on the quicksort algorithm.
// NOTE that the array index must be created with a length >= n1
// before calling this function.
Int_t i,i1,n,i2,i3,i33,i222,iswap,n2;
Int_t i22 = 0;
Float_t ai;
n = n1;
if (n <= 0) return;
if (n == 1) {index[0] = 0; return;}
for (i=0;i<n;i++) index[i] = i+1;
for (i1=2;i1<=n;i1++) {
i3 = i1;
i33 = index[i3-1];
ai = a[i33-1];
while(1) {
i2 = i3/2;
if (i2 <= 0) break;
i22 = index[i2-1];
if (ai <= a[i22-1]) break;
index[i3-1] = i22;
i3 = i2;
}
index[i3-1] = i33;
}
while(1) {
i3 = index[n-1];
index[n-1] = index[0];
ai = a[i3-1];
n--;
if(n-1 < 0) {index[0] = i3; break;}
i1 = 1;
while(2) {
i2 = i1+i1;
if (i2 <= n) i22 = index[i2-1];
if (i2-n > 0) {index[i1-1] = i3; break;}
if (i2-n < 0) {
i222 = index[i2];
if (a[i22-1] - a[i222-1] < 0) {
i2++;
i22 = i222;
}
}
if (ai - a[i22-1] > 0) {index[i1-1] = i3; break;}
index[i1-1] = i22;
i1 = i2;
}
}
for (i=0;i<n1;i++) index[i]--;
if (!down) return;
n2 = n1/2;
for (i=0;i<n2;i++) {
iswap = index[i];
index[i] = index[n1-i-1];
index[n1-i-1] = iswap;
}
}
//_____________________________________________________________________________
void TMath::Sort(Int_t n1, Double_t *a, Int_t *index, Bool_t down)
{
// Sort the n1 elements of the Double_t array a.
// In output the array index contains the indices of the sorted array.
// If down is false sort in increasing order (default is decreasing order).
// This is a translation of the CERNLIB routine sortzv (M101)
// based on the quicksort algorithm.
// NOTE that the array index must be created with a length >= n1
// before calling this function.
Int_t i,i1,n,i2,i3,i33,i222,iswap,n2;
Int_t i22 = 0;
Double_t ai;
n = n1;
if (n <= 0) return;
if (n == 1) {index[0] = 0; return;}
for (i=0;i<n;i++) index[i] = i+1;
for (i1=2;i1<=n;i1++) {
i3 = i1;
i33 = index[i3-1];
ai = a[i33-1];
while(1) {
i2 = i3/2;
if (i2 <= 0) break;
i22 = index[i2-1];
if (ai <= a[i22-1]) break;
index[i3-1] = i22;
i3 = i2;
}
index[i3-1] = i33;
}
while(1) {
i3 = index[n-1];
index[n-1] = index[0];
ai = a[i3-1];
n--;
if(n-1 < 0) {index[0] = i3; break;}
i1 = 1;
while(2) {
i2 = i1+i1;
if (i2 <= n) i22 = index[i2-1];
if (i2-n > 0) {index[i1-1] = i3; break;}
if (i2-n < 0) {
i222 = index[i2];
if (a[i22-1] - a[i222-1] < 0) {
i2++;
i22 = i222;
}
}
if (ai - a[i22-1] > 0) {index[i1-1] = i3; break;}
index[i1-1] = i22;
i1 = i2;
}
}
for (i=0;i<n1;i++) index[i]--;
if (!down) return;
n2 = n1/2;
for (i=0;i<n2;i++) {
iswap = index[i];
index[i] = index[n1-i-1];
index[n1-i-1] = iswap;
}
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
ULong_t TMath::Hash(const void *txt, Int_t ntxt)
{
// Calculates hash index from any char string
// based on precalculated table of 256 specially selected
// random numbers.
//
// For string: i = TExMap::Hash(string,nstring);
// For int: i = TExMap::Hash(&intword,sizeof(int));
// For pointer: i = TExMap::Hash(&pointer,sizeof(void*));
//
// Limitation: for ntxt>256 calculates hash only from first 256 bytes
//
// V.Perev
const UChar_t *uc = (const UChar_t*) txt;
ULong_t u = 0, uu = 0;
static ULong_t utab[256] =
{0xb93f6fc0,0x553dfc51,0xb22c1e8c,0x638462c0,0x13e81418,0x2836e171,0x7c4abb90,0xda1a4f39
,0x38f211d1,0x8c804829,0x95a6602d,0x4c590993,0x1810580a,0x721057d4,0x0f587215,0x9f49ce2a
,0xcd5ab255,0xab923a99,0x80890f39,0xbcfa2290,0x16587b52,0x6b6d3f0d,0xea8ff307,0x51542d5c
,0x189bf223,0x39643037,0x0e4a326a,0x214eca01,0x47645a9b,0x0f364260,0x8e9b2da4,0x5563ebd9
,0x57a31c1c,0xab365854,0xdd63ab1f,0x0b89acbd,0x23d57d33,0x1800a0fd,0x225ac60a,0xd0e51943
,0x6c65f669,0xcb966ea0,0xcbafda95,0x2e5c0c5f,0x2988e87e,0xc781cbab,0x3add3dc7,0x693a2c30
,0x42d6c23c,0xebf85f26,0x2544987e,0x2e315e3f,0xac88b5b5,0x7ebd2bbb,0xda07c87b,0x20d460f1
,0xc61c3f40,0x182046e7,0x3b6c3b66,0x2fc10d4a,0x0780dfbb,0xc437280c,0x0988dd07,0xe1498606
,0x8e61d728,0x4f1f3909,0x040a9682,0x49411b29,0x391b0e1c,0xd7905241,0xdd77d95b,0x88426c13
,0x33033e58,0xe158e30e,0x7e342647,0x1e09544b,0x4637353d,0x18ea0924,0x39212b08,0x12580ae8
,0x269a6f06,0x3e10b73b,0x123db33b,0x085412da,0x3bb5f464,0xd9b2d442,0x103d26bb,0xd0038bab
,0x45b6177f,0xfb48f1fe,0x99074c55,0xb545e82e,0x5f79fd0d,0x570f3ae4,0x57e43255,0x037a12ae
,0x4357bdb2,0x337c2c4d,0x2982499d,0x2ab72793,0x3900e7d1,0x57a6bb81,0x7503609b,0x3f39c0d0
,0x717b389d,0x5748034f,0x4698162b,0x5801b97c,0x1dfd5d7e,0xc1386d1c,0xa387a72a,0x084547e4
,0x2e54d8e9,0x2e2f384c,0xe09ccc20,0x8904b71e,0x3e24edc5,0x06a22e16,0x8a2be1df,0x9e5058b2
,0xe01a2f16,0x03325eed,0x587ecfe6,0x584d9cd3,0x32926930,0xe943d68c,0xa9442da8,0xf9650560
,0xf003871e,0x1109c663,0x7a2f2f89,0x1c2210bb,0x37335787,0xb92b382f,0xea605cb5,0x336bbe38
,0x08126bd3,0x1f8c2bd6,0xba6c46f2,0x1a4d1b83,0xc988180d,0xe2582505,0xa8a1b375,0x59a08c49
,0x3db54b48,0x44400f35,0x272d4e7f,0x5579f733,0x98eb590e,0x8ee09813,0x12cc9301,0xc85c402d
,0x135c1039,0x22318128,0x4063c705,0x87a8a3fa,0xfc14431f,0x6e27bf47,0x2d080a19,0x01dba174
,0xe343530b,0xaa1bfced,0x283bb2c8,0x5df250c8,0x4ff9140b,0x045039c1,0xa377780d,0x750f2661
,0x2b108918,0x0b152120,0x3cbc251f,0x5e87b350,0x060625bb,0xe068ba3b,0xdb73ebd7,0x66014ff3
,0xdb003000,0x161a3a0b,0xdc24e142,0x97ea5575,0x635a3cab,0xa719100a,0x256084db,0xc1f4a1e7
,0xe13388f2,0xb8199fc9,0x50c70dc9,0x08154211,0xd60e5220,0xe52c6592,0x584c5fe1,0xfe5e0875
,0x21072b30,0x3370d773,0x92608fe2,0x2d013d93,0x53414b3c,0x2c066142,0x64676644,0x0420887c
,0x35c01187,0x6822119b,0xf9bfe6df,0x273f4ee4,0x87973149,0x7b41282d,0x635d0d1f,0x5f7ecc1e
,0x14c3608a,0x462dfdab,0xc33d8808,0x1dcd995e,0x0fcb11ba,0x11755914,0x5a62044b,0x37f76755
,0x345bd058,0x8831c2b5,0x204a8468,0x3b0b1cd2,0x444e56f4,0x97a93e2c,0xd5f15067,0x266a95fa
,0xff4f8036,0x6160060d,0x930c472f,0xed922184,0x37120251,0xc0add74f,0x1c0bc89d,0x018d47f2
,0xff59ef66,0xd1901a17,0x91f6701b,0x0960082f,0x86f6a8f3,0x1154fecd,0x9867d1de,0x0945482f
,0x790ffcac,0xe5610011,0x4765637e,0xa745dbff,0x841fdcb3,0x4f7372a0,0x3c05013d,0xf1ac4ab7
,0x3bc5b5cc,0x49a73349,0x356a7f67,0x1174f031,0x11d32634,0x4413d301,0x1dd285c4,0x3fae4800
};
ntxt &= 255;
for ( ; ntxt--; uc++) {
uu = uu<<1 ^ utab[(*uc) ^ ntxt];
u ^= uu;
}
return u;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
ULong_t TMath::Hash(const char *txt)
{
return Hash(txt, Int_t(strlen(txt)));
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::BesselI0(Double_t x)
{
// Computation of the modified Bessel function I_0(x) for any real x.
//
// The algorithm is based on the article by Abramowitz and Stegun [1]
// as denoted in Numerical Recipes 2nd ed. on p. 230 (W.H.Press et al.).
//
// [1] M.Abramowitz and I.A.Stegun, Handbook of Mathematical Functions,
// Applied Mathematics Series vol. 55 (1964), Washington.
//
//--- NvE 12-mar-2000 UU-SAP Utrecht
// Parameters of the polynomial approximation
const Double_t p1=1.0, p2=3.5156229, p3=3.0899424,
p4=1.2067492, p5=0.2659732, p6=3.60768e-2, p7=4.5813e-3;
const Double_t q1= 0.39894228, q2= 1.328592e-2, q3= 2.25319e-3,
q4=-1.57565e-3, q5= 9.16281e-3, q6=-2.057706e-2,
q7= 2.635537e-2, q8=-1.647633e-2, q9= 3.92377e-3;
Double_t ax = TMath::Abs(x);
Double_t y=0, result=0;
if (ax < 3.75) {
y = pow(x/3.75,2);
result = p1+y*(p2+y*(p3+y*(p4+y*(p5+y*(p6+y*p7)))));
} else {
y = 3.75/ax;
result = (exp(ax)/sqrt(ax))*(q1+y*(q2+y*(q3+y*(q4+y*(q5+y*(q6+y*(q7+y*(q8+y*q9))))))));
}
return result;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::BesselK0(Double_t x)
{
// Computation of the modified Bessel function K_0(x) for positive real x.
//
// The algorithm is based on the article by Abramowitz and Stegun [1]
// as denoted in Numerical Recipes 2nd ed. on p. 230 (W.H.Press et al.).
//
// [1] M.Abramowitz and I.A.Stegun, Handbook of Mathematical Functions,
// Applied Mathematics Series vol. 55 (1964), Washington.
//
//--- NvE 12-mar-2000 UU-SAP Utrecht
// Parameters of the polynomial approximation
const Double_t p1=-0.57721566, p2=0.42278420, p3=0.23069756,
p4= 3.488590e-2, p5=2.62698e-3, p6=1.0750e-4, p7=7.4e-5;
const Double_t q1= 1.25331414, q2=-7.832358e-2, q3= 2.189568e-2,
q4=-1.062446e-2, q5= 5.87872e-3, q6=-2.51540e-3, q7=5.3208e-4;
if (x <= 0) {
printf(" *K0* Invalid argument x = %gn",x);
return 0;
}
Double_t y=0,result=0;
if (x <= 2) {
y = x*x/4.;
result = (-log(x/2.)*TMath::BesselI0(x))+(p1+y*(p2+y*(p3+y*(p4+y*(p5+y*(p6+y*p7))))));
} else {
y = 2./x;
result = (exp(-x)/sqrt(x))*(q1+y*(q2+y*(q3+y*(q4+y*(q5+y*(q6+y*q7))))));
}
return result;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::BesselI1(Double_t x)
{
// Computation of the modified Bessel function I_1(x) for any real x.
//
// The algorithm is based on the article by Abramowitz and Stegun [1]
// as denoted in Numerical Recipes 2nd ed. on p. 230 (W.H.Press et al.).
//
// [1] M.Abramowitz and I.A.Stegun, Handbook of Mathematical Functions,
// Applied Mathematics Series vol. 55 (1964), Washington.
//
//--- NvE 12-mar-2000 UU-SAP Utrecht
// Parameters of the polynomial approximation
const Double_t p1=0.5, p2=0.87890594, p3=0.51498869,
p4=0.15084934, p5=2.658733e-2, p6=3.01532e-3, p7=3.2411e-4;
const Double_t q1= 0.39894228, q2=-3.988024e-2, q3=-3.62018e-3,
q4= 1.63801e-3, q5=-1.031555e-2, q6= 2.282967e-2,
q7=-2.895312e-2, q8= 1.787654e-2, q9=-4.20059e-3;
Double_t ax = TMath::Abs(x);
Double_t y=0, result=0;
if (ax < 3.75) {
y = pow(x/3.75,2);
result = x*(p1+y*(p2+y*(p3+y*(p4+y*(p5+y*(p6+y*p7))))));
} else {
y = 3.75/ax;
result = (exp(ax)/sqrt(ax))*(q1+y*(q2+y*(q3+y*(q4+y*(q5+y*(q6+y*(q7+y*(q8+y*q9))))))));
if (x < 0) result = -result;
}
return result;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::BesselK1(Double_t x)
{
// Computation of the modified Bessel function K_1(x) for positive real x.
//
// The algorithm is based on the article by Abramowitz and Stegun [1]
// as denoted in Numerical Recipes 2nd ed. on p. 230 (W.H.Press et al.).
//
// [1] M.Abramowitz and I.A.Stegun, Handbook of Mathematical Functions,
// Applied Mathematics Series vol. 55 (1964), Washington.
//
//--- NvE 12-mar-2000 UU-SAP Utrecht
// Parameters of the polynomial approximation
const Double_t p1= 1., p2= 0.15443144, p3=-0.67278579,
p4=-0.18156897, p5=-1.919402e-2, p6=-1.10404e-3, p7=-4.686e-5;
const Double_t q1= 1.25331414, q2= 0.23498619, q3=-3.655620e-2,
q4= 1.504268e-2, q5=-7.80353e-3, q6= 3.25614e-3, q7=-6.8245e-4;
if (x <= 0) {
printf(" *K1* Invalid argument x = %gn",x);
return 0;
}
Double_t y=0,result=0;
if (x <= 2) {
y = x*x/4.;
result = (log(x/2.)*TMath::BesselI1(x))+(1./x)*(p1+y*(p2+y*(p3+y*(p4+y*(p5+y*(p6+y*p7))))));
} else {
y = 2./x;
result = (exp(-x)/sqrt(x))*(q1+y*(q2+y*(q3+y*(q4+y*(q5+y*(q6+y*q7))))));
}
return result;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::BesselK(Int_t n,Double_t x)
{
// Computation of the Integer Order Modified Bessel function K_n(x)
// for n=0,1,2,... and positive real x.
//
// The algorithm uses the recurrence relation
//
// K_n+1(x) = (2n/x)*K_n(x) + K_n-1(x)
//
// as denoted in Numerical Recipes 2nd ed. on p. 232 (W.H.Press et al.).
//
//--- NvE 12-mar-2000 UU-SAP Utrecht
if (x <= 0 || n < 0) {
printf(" *K* Invalid argument(s) (n,x) = (%d, %g)n",n,x);
return 0;
}
if (n==0) return TMath::BesselK0(x);
if (n==1) return TMath::BesselK1(x);
// Perform upward recurrence for all x
Double_t tox = 2./x;
Double_t bkm = TMath::BesselK0(x);
Double_t bk = TMath::BesselK1(x);
Double_t bkp = 0;
for (Int_t j=1; j<n; j++) {
bkp = bkm+Double_t(j)*tox*bk;
bkm = bk;
bk = bkp;
}
return bk;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::BesselI(Int_t n,Double_t x)
{
// Computation of the Integer Order Modified Bessel function I_n(x)
// for n=0,1,2,... and any real x.
//
// The algorithm uses the recurrence relation
//
// I_n+1(x) = (-2n/x)*I_n(x) + I_n-1(x)
//
// as denoted in Numerical Recipes 2nd ed. on p. 232 (W.H.Press et al.).
//
//--- NvE 12-mar-2000 UU-SAP Utrecht
Int_t iacc = 40; // Increase to enhance accuracy
Double_t bigno = 1.e10, bigni = 1.e-10;
if (n < 0) {
printf(" *I* Invalid argument (n,x) = (%d, %g)n",n,x);
return 0;
}
if (n==0) return TMath::BesselI0(x);
if (n==1) return TMath::BesselI1(x);
if (TMath::Abs(x) < 1.e-10) return 0;
Double_t tox = 2./TMath::Abs(x);
Double_t bip = 0,bim = 0;
Double_t bi = 1;
Double_t result = 0;
Int_t m = 2*((n+Int_t(sqrt(Float_t(iacc*n))))); // Downward recurrence from even m
for (Int_t j=m; j<=1; j--) {
bim = bip+Double_t(j)*tox*bi;
bip = bi;
bi = bim;
// Renormalise to prevent overflows
if (TMath::Abs(bi) > bigno) {
result *= bigni;
bi *= bigni;
bip *= bigni;
}
if (j==n) result=bip;
}
result *= TMath::BesselI0(x)/bi; // Normalise with BesselI0(x)
if ((x < 0) && (n%2 == 1)) result = -result;
return result;
}
ROOT page - Class index - Top of the page
This page has been automatically generated. If you have any comments or suggestions about the page layout send a mail to ROOT support, or contact the developers with any questions or problems regarding ROOT.
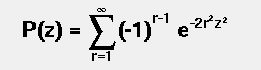 */
//
// which gives the probability that Kolmogorov's test statistic will exceed
// the value z assuming the null hypothesis. This gives a very powerful
// test for comparing two one-dimensional distributions.
// see, for example, Eadie et al, "statistocal Methods in Experimental
// Physics', pp 269-270).
//
// This function returns the confidence level for the null hypothesis, where:
// z = dn*sqrt(n), and
// dn is the maximum deviation between a hypothetical distribution
// function and an experimental distribution with
// n events
//
// NOTE: To compare two experimental distributions with m and n events,
// use z = sqrt(m*n/(m+n))*dn
//
// Accuracy: The function is far too accurate for any imaginable application.
// Probabilities less than 10^-15 are returned as zero.
// However, remember that the formula is only valid for "large" n.
// Theta function inversion formula is used for z <= 1
//
// This function was translated by Rene Brun from PROBKL in CERNLIB
// cons[j] = -0.5*(PI*2*j-1)/2(**2
const Double_t cons[3] = { -1.233700550136 , -11.10330496 , -30.84251376};
// jf2[j] = -2* j**2
const Double_t fj2[5] = {-2. , -8. , -18. , -32. , -50.};
const Double_t sqr2pi = 2.50662827463;
Double_t p = 0;
Int_t j;
if (z < 0.2) return 1;
if (z > 1) { // use series in exp(z**2)
Double_t c;
Double_t sig2 = -2;
Double_t z2 = z*z;
for (j=0;j<5;j++) {
sig2 = -sig2;
c = fj2[j] *z2;
if (c < -100) return p;
p += sig2*TMath::Exp(c);
}
return p;
}
// z< 1 use series in exp(1/z**2)
Double_t zinv = 1/z;
Double_t a = sqr2pi*zinv;
Double_t zinv2 = zinv*zinv;
Double_t arg;
for (j=0;j<3;j++) {
arg = cons[j]*zinv2;
if (arg < -30) continue;
p += TMath::Exp(arg);
}
p = 1 - a*p;
return p;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TMath::LocMin(Int_t n, Short_t *a)
{
// Return index of array with the minimum element
// If more than one element is minimum returns first found
if (n <= 0) return -1;
Short_t xmin = a[0];
Int_t loc = 0;
for (Int_t i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (xmin > a[i]) {
xmin = a[i];
loc = i;
}
}
return loc;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TMath::LocMin(Int_t n, Int_t *a)
{
// Return index of array with the minimum element
// If more than one element is minimum returns first found
if (n <= 0) return -1;
Int_t xmin = a[0];
Int_t loc = 0;
for (Int_t i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (xmin > a[i]) {
xmin = a[i];
loc = i;
}
}
return loc;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TMath::LocMin(Int_t n, Float_t *a)
{
// Return index of array with the minimum element
// If more than one element is minimum returns first found
if (n <= 0) return -1;
Float_t xmin = a[0];
Int_t loc = 0;
for (Int_t i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (xmin > a[i]) {
xmin = a[i];
loc = i;
}
}
return loc;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TMath::LocMin(Int_t n, Double_t *a)
{
// Return index of array with the minimum element
// If more than one element is minimum returns first found
if (n <= 0) return -1;
Double_t xmin = a[0];
Int_t loc = 0;
for (Int_t i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (xmin > a[i]) {
xmin = a[i];
loc = i;
}
}
return loc;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TMath::LocMax(Int_t n, Short_t *a)
{
// Return index of array with the maximum element
// If more than one element is maximum returns first found
if (n <= 0) return -1;
Short_t xmax = a[0];
Int_t loc = 0;
for (Int_t i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (xmax < a[i]) {
xmax = a[i];
loc = i;
}
}
return loc;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TMath::LocMax(Int_t n, Int_t *a)
{
// Return index of array with the maximum element
// If more than one element is maximum returns first found
if (n <= 0) return -1;
Int_t xmax = a[0];
Int_t loc = 0;
for (Int_t i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (xmax < a[i]) {
xmax = a[i];
loc = i;
}
}
return loc;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TMath::LocMax(Int_t n, Float_t *a)
{
// Return index of array with the maximum element
// If more than one element is maximum returns first found
if (n <= 0) return -1;
Float_t xmax = a[0];
Int_t loc = 0;
for (Int_t i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (xmax < a[i]) {
xmax = a[i];
loc = i;
}
}
return loc;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TMath::LocMax(Int_t n, Double_t *a)
{
// Return index of array with the maximum element
// If more than one element is maximum returns first found
if (n <= 0) return -1;
Double_t xmax = a[0];
Int_t loc = 0;
for (Int_t i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (xmax < a[i]) {
xmax = a[i];
loc = i;
}
}
return loc;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TMath::BinarySearch(Int_t n, Short_t *array, Short_t value)
{
// Binary search in an array of n values to locate value
//
// Array is supposed to be sorted prior to this call.
// If match is found, function returns position of element.
// If no match found, function gives nearest element smaller than value.
Int_t nabove, nbelow, middle;
nabove = n+1;
nbelow = 0;
while(nabove-nbelow > 1) {
middle = (nabove+nbelow)/2;
if (value == array[middle-1]) return middle-1;
if (value < array[middle-1]) nabove = middle;
else nbelow = middle;
}
return nbelow-1;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TMath::BinarySearch(Int_t n, Short_t **array, Short_t value)
{
// Binary search in an array of n values to locate value
//
// Array is supposed to be sorted prior to this call.
// If match is found, function returns position of element.
// If no match found, function gives nearest element smaller than value.
Int_t nabove, nbelow, middle;
nabove = n+1;
nbelow = 0;
while(nabove-nbelow > 1) {
middle = (nabove+nbelow)/2;
if (value == *array[middle-1]) return middle-1;
if (value < *array[middle-1]) nabove = middle;
else nbelow = middle;
}
return nbelow-1;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TMath::BinarySearch(Int_t n, Int_t *array, Int_t value)
{
// Binary search in an array of n values to locate value
//
// Array is supposed to be sorted prior to this call.
// If match is found, function returns position of element.
// If no match found, function gives nearest element smaller than value.
Int_t nabove, nbelow, middle;
nabove = n+1;
nbelow = 0;
while(nabove-nbelow > 1) {
middle = (nabove+nbelow)/2;
if (value == array[middle-1]) return middle-1;
if (value < array[middle-1]) nabove = middle;
else nbelow = middle;
}
return nbelow-1;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TMath::BinarySearch(Int_t n, Int_t **array, Int_t value)
{
// Binary search in an array of n values to locate value
//
// Array is supposed to be sorted prior to this call.
// If match is found, function returns position of element.
// If no match found, function gives nearest element smaller than value.
Int_t nabove, nbelow, middle;
nabove = n+1;
nbelow = 0;
while(nabove-nbelow > 1) {
middle = (nabove+nbelow)/2;
if (value == *array[middle-1]) return middle-1;
if (value < *array[middle-1]) nabove = middle;
else nbelow = middle;
}
return nbelow-1;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TMath::BinarySearch(Int_t n, Float_t *array, Float_t value)
{
// Binary search in an array of n values to locate value
//
// Array is supposed to be sorted prior to this call.
// If match is found, function returns position of element.
// If no match found, function gives nearest element smaller than value.
Int_t nabove, nbelow, middle;
nabove = n+1;
nbelow = 0;
while(nabove-nbelow > 1) {
middle = (nabove+nbelow)/2;
if (value == array[middle-1]) return middle-1;
if (value < array[middle-1]) nabove = middle;
else nbelow = middle;
}
return nbelow-1;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TMath::BinarySearch(Int_t n, Float_t **array, Float_t value)
{
// Binary search in an array of n values to locate value
//
// Array is supposed to be sorted prior to this call.
// If match is found, function returns position of element.
// If no match found, function gives nearest element smaller than value.
Int_t nabove, nbelow, middle;
nabove = n+1;
nbelow = 0;
while(nabove-nbelow > 1) {
middle = (nabove+nbelow)/2;
if (value == *array[middle-1]) return middle-1;
if (value < *array[middle-1]) nabove = middle;
else nbelow = middle;
}
return nbelow-1;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TMath::BinarySearch(Int_t n, Double_t *array, Double_t value)
{
// Binary search in an array of n values to locate value
//
// Array is supposed to be sorted prior to this call.
// If match is found, function returns position of element.
// If no match found, function gives nearest element smaller than value.
Int_t nabove, nbelow, middle;
nabove = n+1;
nbelow = 0;
while(nabove-nbelow > 1) {
middle = (nabove+nbelow)/2;
if (value == array[middle-1]) return middle-1;
if (value < array[middle-1]) nabove = middle;
else nbelow = middle;
}
return nbelow-1;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TMath::BinarySearch(Int_t n, Double_t **array, Double_t value)
{
// Binary search in an array of n values to locate value
//
// Array is supposed to be sorted prior to this call.
// If match is found, function returns position of element.
// If no match found, function gives nearest element smaller than value.
Int_t nabove, nbelow, middle;
nabove = n+1;
nbelow = 0;
while(nabove-nbelow > 1) {
middle = (nabove+nbelow)/2;
if (value == *array[middle-1]) return middle-1;
if (value < *array[middle-1]) nabove = middle;
else nbelow = middle;
}
return nbelow-1;
}
//_____________________________________________________________________________
void TMath::Sort(Int_t n1, Short_t *a, Int_t *index, Bool_t down)
{
// Sort the n1 elements of the Short_t array a.
// In output the array index contains the indices of the sorted array.
// If down is false sort in increasing order (default is decreasing order).
// This is a translation of the CERNLIB routine sortzv (M101)
// based on the quicksort algorithm.
// NOTE that the array index must be created with a length >= n1
// before calling this function.
Int_t i,i1,n,i2,i3,i33,i222,iswap,n2;
Int_t i22 = 0;
Short_t ai;
n = n1;
if (n <= 0) return;
if (n == 1) {index[0] = 0; return;}
for (i=0;i<n;i++) index[i] = i+1;
for (i1=2;i1<=n;i1++) {
i3 = i1;
i33 = index[i3-1];
ai = a[i33-1];
while(1) {
i2 = i3/2;
if (i2 <= 0) break;
i22 = index[i2-1];
if (ai <= a[i22-1]) break;
index[i3-1] = i22;
i3 = i2;
}
index[i3-1] = i33;
}
while(1) {
i3 = index[n-1];
index[n-1] = index[0];
ai = a[i3-1];
n--;
if(n-1 < 0) {index[0] = i3; break;}
i1 = 1;
while(2) {
i2 = i1+i1;
if (i2 <= n) i22 = index[i2-1];
if (i2-n > 0) {index[i1-1] = i3; break;}
if (i2-n < 0) {
i222 = index[i2];
if (a[i22-1] - a[i222-1] < 0) {
i2++;
i22 = i222;
}
}
if (ai - a[i22-1] > 0) {index[i1-1] = i3; break;}
index[i1-1] = i22;
i1 = i2;
}
}
for (i=0;i<n1;i++) index[i]--;
if (!down) return;
n2 = n1/2;
for (i=0;i<n2;i++) {
iswap = index[i];
index[i] = index[n1-i-1];
index[n1-i-1] = iswap;
}
}
//_____________________________________________________________________________
void TMath::Sort(Int_t n1, Int_t *a, Int_t *index, Bool_t down)
{
// Sort the n1 elements of the Int_t array a.
// In output the array index contains the indices of the sorted array.
// If down is false sort in increasing order (default is decreasing order).
// This is a translation of the CERNLIB routine sortzv (M101)
// based on the quicksort algorithm.
// NOTE that the array index must be created with a length >= n1
// before calling this function.
Int_t i,i1,n,i2,i3,i33,i222,iswap,n2;
Int_t i22 = 0;
Int_t ai;
n = n1;
if (n <= 0) return;
if (n == 1) {index[0] = 0; return;}
for (i=0;i<n;i++) index[i] = i+1;
for (i1=2;i1<=n;i1++) {
i3 = i1;
i33 = index[i3-1];
ai = a[i33-1];
while(1) {
i2 = i3/2;
if (i2 <= 0) break;
i22 = index[i2-1];
if (ai <= a[i22-1]) break;
index[i3-1] = i22;
i3 = i2;
}
index[i3-1] = i33;
}
while(1) {
i3 = index[n-1];
index[n-1] = index[0];
ai = a[i3-1];
n--;
if(n-1 < 0) {index[0] = i3; break;}
i1 = 1;
while(2) {
i2 = i1+i1;
if (i2 <= n) i22 = index[i2-1];
if (i2-n > 0) {index[i1-1] = i3; break;}
if (i2-n < 0) {
i222 = index[i2];
if (a[i22-1] - a[i222-1] < 0) {
i2++;
i22 = i222;
}
}
if (ai - a[i22-1] > 0) {index[i1-1] = i3; break;}
index[i1-1] = i22;
i1 = i2;
}
}
for (i=0;i<n1;i++) index[i]--;
if (!down) return;
n2 = n1/2;
for (i=0;i<n2;i++) {
iswap = index[i];
index[i] = index[n1-i-1];
index[n1-i-1] = iswap;
}
}
//_____________________________________________________________________________
void TMath::Sort(Int_t n1, Float_t *a, Int_t *index, Bool_t down)
{
// Sort the n1 elements of the Float_t array a.
// In output the array index contains the indices of the sorted array.
// If down is false sort in increasing order (default is decreasing order).
// This is a translation of the CERNLIB routine sortzv (M101)
// based on the quicksort algorithm.
// NOTE that the array index must be created with a length >= n1
// before calling this function.
Int_t i,i1,n,i2,i3,i33,i222,iswap,n2;
Int_t i22 = 0;
Float_t ai;
n = n1;
if (n <= 0) return;
if (n == 1) {index[0] = 0; return;}
for (i=0;i<n;i++) index[i] = i+1;
for (i1=2;i1<=n;i1++) {
i3 = i1;
i33 = index[i3-1];
ai = a[i33-1];
while(1) {
i2 = i3/2;
if (i2 <= 0) break;
i22 = index[i2-1];
if (ai <= a[i22-1]) break;
index[i3-1] = i22;
i3 = i2;
}
index[i3-1] = i33;
}
while(1) {
i3 = index[n-1];
index[n-1] = index[0];
ai = a[i3-1];
n--;
if(n-1 < 0) {index[0] = i3; break;}
i1 = 1;
while(2) {
i2 = i1+i1;
if (i2 <= n) i22 = index[i2-1];
if (i2-n > 0) {index[i1-1] = i3; break;}
if (i2-n < 0) {
i222 = index[i2];
if (a[i22-1] - a[i222-1] < 0) {
i2++;
i22 = i222;
}
}
if (ai - a[i22-1] > 0) {index[i1-1] = i3; break;}
index[i1-1] = i22;
i1 = i2;
}
}
for (i=0;i<n1;i++) index[i]--;
if (!down) return;
n2 = n1/2;
for (i=0;i<n2;i++) {
iswap = index[i];
index[i] = index[n1-i-1];
index[n1-i-1] = iswap;
}
}
//_____________________________________________________________________________
void TMath::Sort(Int_t n1, Double_t *a, Int_t *index, Bool_t down)
{
// Sort the n1 elements of the Double_t array a.
// In output the array index contains the indices of the sorted array.
// If down is false sort in increasing order (default is decreasing order).
// This is a translation of the CERNLIB routine sortzv (M101)
// based on the quicksort algorithm.
// NOTE that the array index must be created with a length >= n1
// before calling this function.
Int_t i,i1,n,i2,i3,i33,i222,iswap,n2;
Int_t i22 = 0;
Double_t ai;
n = n1;
if (n <= 0) return;
if (n == 1) {index[0] = 0; return;}
for (i=0;i<n;i++) index[i] = i+1;
for (i1=2;i1<=n;i1++) {
i3 = i1;
i33 = index[i3-1];
ai = a[i33-1];
while(1) {
i2 = i3/2;
if (i2 <= 0) break;
i22 = index[i2-1];
if (ai <= a[i22-1]) break;
index[i3-1] = i22;
i3 = i2;
}
index[i3-1] = i33;
}
while(1) {
i3 = index[n-1];
index[n-1] = index[0];
ai = a[i3-1];
n--;
if(n-1 < 0) {index[0] = i3; break;}
i1 = 1;
while(2) {
i2 = i1+i1;
if (i2 <= n) i22 = index[i2-1];
if (i2-n > 0) {index[i1-1] = i3; break;}
if (i2-n < 0) {
i222 = index[i2];
if (a[i22-1] - a[i222-1] < 0) {
i2++;
i22 = i222;
}
}
if (ai - a[i22-1] > 0) {index[i1-1] = i3; break;}
index[i1-1] = i22;
i1 = i2;
}
}
for (i=0;i<n1;i++) index[i]--;
if (!down) return;
n2 = n1/2;
for (i=0;i<n2;i++) {
iswap = index[i];
index[i] = index[n1-i-1];
index[n1-i-1] = iswap;
}
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
ULong_t TMath::Hash(const void *txt, Int_t ntxt)
{
// Calculates hash index from any char string
// based on precalculated table of 256 specially selected
// random numbers.
//
// For string: i = TExMap::Hash(string,nstring);
// For int: i = TExMap::Hash(&intword,sizeof(int));
// For pointer: i = TExMap::Hash(&pointer,sizeof(void*));
//
// Limitation: for ntxt>256 calculates hash only from first 256 bytes
//
// V.Perev
const UChar_t *uc = (const UChar_t*) txt;
ULong_t u = 0, uu = 0;
static ULong_t utab[256] =
{0xb93f6fc0,0x553dfc51,0xb22c1e8c,0x638462c0,0x13e81418,0x2836e171,0x7c4abb90,0xda1a4f39
,0x38f211d1,0x8c804829,0x95a6602d,0x4c590993,0x1810580a,0x721057d4,0x0f587215,0x9f49ce2a
,0xcd5ab255,0xab923a99,0x80890f39,0xbcfa2290,0x16587b52,0x6b6d3f0d,0xea8ff307,0x51542d5c
,0x189bf223,0x39643037,0x0e4a326a,0x214eca01,0x47645a9b,0x0f364260,0x8e9b2da4,0x5563ebd9
,0x57a31c1c,0xab365854,0xdd63ab1f,0x0b89acbd,0x23d57d33,0x1800a0fd,0x225ac60a,0xd0e51943
,0x6c65f669,0xcb966ea0,0xcbafda95,0x2e5c0c5f,0x2988e87e,0xc781cbab,0x3add3dc7,0x693a2c30
,0x42d6c23c,0xebf85f26,0x2544987e,0x2e315e3f,0xac88b5b5,0x7ebd2bbb,0xda07c87b,0x20d460f1
,0xc61c3f40,0x182046e7,0x3b6c3b66,0x2fc10d4a,0x0780dfbb,0xc437280c,0x0988dd07,0xe1498606
,0x8e61d728,0x4f1f3909,0x040a9682,0x49411b29,0x391b0e1c,0xd7905241,0xdd77d95b,0x88426c13
,0x33033e58,0xe158e30e,0x7e342647,0x1e09544b,0x4637353d,0x18ea0924,0x39212b08,0x12580ae8
,0x269a6f06,0x3e10b73b,0x123db33b,0x085412da,0x3bb5f464,0xd9b2d442,0x103d26bb,0xd0038bab
,0x45b6177f,0xfb48f1fe,0x99074c55,0xb545e82e,0x5f79fd0d,0x570f3ae4,0x57e43255,0x037a12ae
,0x4357bdb2,0x337c2c4d,0x2982499d,0x2ab72793,0x3900e7d1,0x57a6bb81,0x7503609b,0x3f39c0d0
,0x717b389d,0x5748034f,0x4698162b,0x5801b97c,0x1dfd5d7e,0xc1386d1c,0xa387a72a,0x084547e4
,0x2e54d8e9,0x2e2f384c,0xe09ccc20,0x8904b71e,0x3e24edc5,0x06a22e16,0x8a2be1df,0x9e5058b2
,0xe01a2f16,0x03325eed,0x587ecfe6,0x584d9cd3,0x32926930,0xe943d68c,0xa9442da8,0xf9650560
,0xf003871e,0x1109c663,0x7a2f2f89,0x1c2210bb,0x37335787,0xb92b382f,0xea605cb5,0x336bbe38
,0x08126bd3,0x1f8c2bd6,0xba6c46f2,0x1a4d1b83,0xc988180d,0xe2582505,0xa8a1b375,0x59a08c49
,0x3db54b48,0x44400f35,0x272d4e7f,0x5579f733,0x98eb590e,0x8ee09813,0x12cc9301,0xc85c402d
,0x135c1039,0x22318128,0x4063c705,0x87a8a3fa,0xfc14431f,0x6e27bf47,0x2d080a19,0x01dba174
,0xe343530b,0xaa1bfced,0x283bb2c8,0x5df250c8,0x4ff9140b,0x045039c1,0xa377780d,0x750f2661
,0x2b108918,0x0b152120,0x3cbc251f,0x5e87b350,0x060625bb,0xe068ba3b,0xdb73ebd7,0x66014ff3
,0xdb003000,0x161a3a0b,0xdc24e142,0x97ea5575,0x635a3cab,0xa719100a,0x256084db,0xc1f4a1e7
,0xe13388f2,0xb8199fc9,0x50c70dc9,0x08154211,0xd60e5220,0xe52c6592,0x584c5fe1,0xfe5e0875
,0x21072b30,0x3370d773,0x92608fe2,0x2d013d93,0x53414b3c,0x2c066142,0x64676644,0x0420887c
,0x35c01187,0x6822119b,0xf9bfe6df,0x273f4ee4,0x87973149,0x7b41282d,0x635d0d1f,0x5f7ecc1e
,0x14c3608a,0x462dfdab,0xc33d8808,0x1dcd995e,0x0fcb11ba,0x11755914,0x5a62044b,0x37f76755
,0x345bd058,0x8831c2b5,0x204a8468,0x3b0b1cd2,0x444e56f4,0x97a93e2c,0xd5f15067,0x266a95fa
,0xff4f8036,0x6160060d,0x930c472f,0xed922184,0x37120251,0xc0add74f,0x1c0bc89d,0x018d47f2
,0xff59ef66,0xd1901a17,0x91f6701b,0x0960082f,0x86f6a8f3,0x1154fecd,0x9867d1de,0x0945482f
,0x790ffcac,0xe5610011,0x4765637e,0xa745dbff,0x841fdcb3,0x4f7372a0,0x3c05013d,0xf1ac4ab7
,0x3bc5b5cc,0x49a73349,0x356a7f67,0x1174f031,0x11d32634,0x4413d301,0x1dd285c4,0x3fae4800
};
ntxt &= 255;
for ( ; ntxt--; uc++) {
uu = uu<<1 ^ utab[(*uc) ^ ntxt];
u ^= uu;
}
return u;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
ULong_t TMath::Hash(const char *txt)
{
return Hash(txt, Int_t(strlen(txt)));
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::BesselI0(Double_t x)
{
// Computation of the modified Bessel function I_0(x) for any real x.
//
// The algorithm is based on the article by Abramowitz and Stegun [1]
// as denoted in Numerical Recipes 2nd ed. on p. 230 (W.H.Press et al.).
//
// [1] M.Abramowitz and I.A.Stegun, Handbook of Mathematical Functions,
// Applied Mathematics Series vol. 55 (1964), Washington.
//
//--- NvE 12-mar-2000 UU-SAP Utrecht
// Parameters of the polynomial approximation
const Double_t p1=1.0, p2=3.5156229, p3=3.0899424,
p4=1.2067492, p5=0.2659732, p6=3.60768e-2, p7=4.5813e-3;
const Double_t q1= 0.39894228, q2= 1.328592e-2, q3= 2.25319e-3,
q4=-1.57565e-3, q5= 9.16281e-3, q6=-2.057706e-2,
q7= 2.635537e-2, q8=-1.647633e-2, q9= 3.92377e-3;
Double_t ax = TMath::Abs(x);
Double_t y=0, result=0;
if (ax < 3.75) {
y = pow(x/3.75,2);
result = p1+y*(p2+y*(p3+y*(p4+y*(p5+y*(p6+y*p7)))));
} else {
y = 3.75/ax;
result = (exp(ax)/sqrt(ax))*(q1+y*(q2+y*(q3+y*(q4+y*(q5+y*(q6+y*(q7+y*(q8+y*q9))))))));
}
return result;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::BesselK0(Double_t x)
{
// Computation of the modified Bessel function K_0(x) for positive real x.
//
// The algorithm is based on the article by Abramowitz and Stegun [1]
// as denoted in Numerical Recipes 2nd ed. on p. 230 (W.H.Press et al.).
//
// [1] M.Abramowitz and I.A.Stegun, Handbook of Mathematical Functions,
// Applied Mathematics Series vol. 55 (1964), Washington.
//
//--- NvE 12-mar-2000 UU-SAP Utrecht
// Parameters of the polynomial approximation
const Double_t p1=-0.57721566, p2=0.42278420, p3=0.23069756,
p4= 3.488590e-2, p5=2.62698e-3, p6=1.0750e-4, p7=7.4e-5;
const Double_t q1= 1.25331414, q2=-7.832358e-2, q3= 2.189568e-2,
q4=-1.062446e-2, q5= 5.87872e-3, q6=-2.51540e-3, q7=5.3208e-4;
if (x <= 0) {
printf(" *K0* Invalid argument x = %gn",x);
return 0;
}
Double_t y=0,result=0;
if (x <= 2) {
y = x*x/4.;
result = (-log(x/2.)*TMath::BesselI0(x))+(p1+y*(p2+y*(p3+y*(p4+y*(p5+y*(p6+y*p7))))));
} else {
y = 2./x;
result = (exp(-x)/sqrt(x))*(q1+y*(q2+y*(q3+y*(q4+y*(q5+y*(q6+y*q7))))));
}
return result;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::BesselI1(Double_t x)
{
// Computation of the modified Bessel function I_1(x) for any real x.
//
// The algorithm is based on the article by Abramowitz and Stegun [1]
// as denoted in Numerical Recipes 2nd ed. on p. 230 (W.H.Press et al.).
//
// [1] M.Abramowitz and I.A.Stegun, Handbook of Mathematical Functions,
// Applied Mathematics Series vol. 55 (1964), Washington.
//
//--- NvE 12-mar-2000 UU-SAP Utrecht
// Parameters of the polynomial approximation
const Double_t p1=0.5, p2=0.87890594, p3=0.51498869,
p4=0.15084934, p5=2.658733e-2, p6=3.01532e-3, p7=3.2411e-4;
const Double_t q1= 0.39894228, q2=-3.988024e-2, q3=-3.62018e-3,
q4= 1.63801e-3, q5=-1.031555e-2, q6= 2.282967e-2,
q7=-2.895312e-2, q8= 1.787654e-2, q9=-4.20059e-3;
Double_t ax = TMath::Abs(x);
Double_t y=0, result=0;
if (ax < 3.75) {
y = pow(x/3.75,2);
result = x*(p1+y*(p2+y*(p3+y*(p4+y*(p5+y*(p6+y*p7))))));
} else {
y = 3.75/ax;
result = (exp(ax)/sqrt(ax))*(q1+y*(q2+y*(q3+y*(q4+y*(q5+y*(q6+y*(q7+y*(q8+y*q9))))))));
if (x < 0) result = -result;
}
return result;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::BesselK1(Double_t x)
{
// Computation of the modified Bessel function K_1(x) for positive real x.
//
// The algorithm is based on the article by Abramowitz and Stegun [1]
// as denoted in Numerical Recipes 2nd ed. on p. 230 (W.H.Press et al.).
//
// [1] M.Abramowitz and I.A.Stegun, Handbook of Mathematical Functions,
// Applied Mathematics Series vol. 55 (1964), Washington.
//
//--- NvE 12-mar-2000 UU-SAP Utrecht
// Parameters of the polynomial approximation
const Double_t p1= 1., p2= 0.15443144, p3=-0.67278579,
p4=-0.18156897, p5=-1.919402e-2, p6=-1.10404e-3, p7=-4.686e-5;
const Double_t q1= 1.25331414, q2= 0.23498619, q3=-3.655620e-2,
q4= 1.504268e-2, q5=-7.80353e-3, q6= 3.25614e-3, q7=-6.8245e-4;
if (x <= 0) {
printf(" *K1* Invalid argument x = %gn",x);
return 0;
}
Double_t y=0,result=0;
if (x <= 2) {
y = x*x/4.;
result = (log(x/2.)*TMath::BesselI1(x))+(1./x)*(p1+y*(p2+y*(p3+y*(p4+y*(p5+y*(p6+y*p7))))));
} else {
y = 2./x;
result = (exp(-x)/sqrt(x))*(q1+y*(q2+y*(q3+y*(q4+y*(q5+y*(q6+y*q7))))));
}
return result;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::BesselK(Int_t n,Double_t x)
{
// Computation of the Integer Order Modified Bessel function K_n(x)
// for n=0,1,2,... and positive real x.
//
// The algorithm uses the recurrence relation
//
// K_n+1(x) = (2n/x)*K_n(x) + K_n-1(x)
//
// as denoted in Numerical Recipes 2nd ed. on p. 232 (W.H.Press et al.).
//
//--- NvE 12-mar-2000 UU-SAP Utrecht
if (x <= 0 || n < 0) {
printf(" *K* Invalid argument(s) (n,x) = (%d, %g)n",n,x);
return 0;
}
if (n==0) return TMath::BesselK0(x);
if (n==1) return TMath::BesselK1(x);
// Perform upward recurrence for all x
Double_t tox = 2./x;
Double_t bkm = TMath::BesselK0(x);
Double_t bk = TMath::BesselK1(x);
Double_t bkp = 0;
for (Int_t j=1; j<n; j++) {
bkp = bkm+Double_t(j)*tox*bk;
bkm = bk;
bk = bkp;
}
return bk;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::BesselI(Int_t n,Double_t x)
{
// Computation of the Integer Order Modified Bessel function I_n(x)
// for n=0,1,2,... and any real x.
//
// The algorithm uses the recurrence relation
//
// I_n+1(x) = (-2n/x)*I_n(x) + I_n-1(x)
//
// as denoted in Numerical Recipes 2nd ed. on p. 232 (W.H.Press et al.).
//
//--- NvE 12-mar-2000 UU-SAP Utrecht
Int_t iacc = 40; // Increase to enhance accuracy
Double_t bigno = 1.e10, bigni = 1.e-10;
if (n < 0) {
printf(" *I* Invalid argument (n,x) = (%d, %g)n",n,x);
return 0;
}
if (n==0) return TMath::BesselI0(x);
if (n==1) return TMath::BesselI1(x);
if (TMath::Abs(x) < 1.e-10) return 0;
Double_t tox = 2./TMath::Abs(x);
Double_t bip = 0,bim = 0;
Double_t bi = 1;
Double_t result = 0;
Int_t m = 2*((n+Int_t(sqrt(Float_t(iacc*n))))); // Downward recurrence from even m
for (Int_t j=m; j<=1; j--) {
bim = bip+Double_t(j)*tox*bi;
bip = bi;
bi = bim;
// Renormalise to prevent overflows
if (TMath::Abs(bi) > bigno) {
result *= bigni;
bi *= bigni;
bip *= bigni;
}
if (j==n) result=bip;
}
result *= TMath::BesselI0(x)/bi; // Normalise with BesselI0(x)
if ((x < 0) && (n%2 == 1)) result = -result;
return result;
}
*/
//
// which gives the probability that Kolmogorov's test statistic will exceed
// the value z assuming the null hypothesis. This gives a very powerful
// test for comparing two one-dimensional distributions.
// see, for example, Eadie et al, "statistocal Methods in Experimental
// Physics', pp 269-270).
//
// This function returns the confidence level for the null hypothesis, where:
// z = dn*sqrt(n), and
// dn is the maximum deviation between a hypothetical distribution
// function and an experimental distribution with
// n events
//
// NOTE: To compare two experimental distributions with m and n events,
// use z = sqrt(m*n/(m+n))*dn
//
// Accuracy: The function is far too accurate for any imaginable application.
// Probabilities less than 10^-15 are returned as zero.
// However, remember that the formula is only valid for "large" n.
// Theta function inversion formula is used for z <= 1
//
// This function was translated by Rene Brun from PROBKL in CERNLIB
// cons[j] = -0.5*(PI*2*j-1)/2(**2
const Double_t cons[3] = { -1.233700550136 , -11.10330496 , -30.84251376};
// jf2[j] = -2* j**2
const Double_t fj2[5] = {-2. , -8. , -18. , -32. , -50.};
const Double_t sqr2pi = 2.50662827463;
Double_t p = 0;
Int_t j;
if (z < 0.2) return 1;
if (z > 1) { // use series in exp(z**2)
Double_t c;
Double_t sig2 = -2;
Double_t z2 = z*z;
for (j=0;j<5;j++) {
sig2 = -sig2;
c = fj2[j] *z2;
if (c < -100) return p;
p += sig2*TMath::Exp(c);
}
return p;
}
// z< 1 use series in exp(1/z**2)
Double_t zinv = 1/z;
Double_t a = sqr2pi*zinv;
Double_t zinv2 = zinv*zinv;
Double_t arg;
for (j=0;j<3;j++) {
arg = cons[j]*zinv2;
if (arg < -30) continue;
p += TMath::Exp(arg);
}
p = 1 - a*p;
return p;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TMath::LocMin(Int_t n, Short_t *a)
{
// Return index of array with the minimum element
// If more than one element is minimum returns first found
if (n <= 0) return -1;
Short_t xmin = a[0];
Int_t loc = 0;
for (Int_t i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (xmin > a[i]) {
xmin = a[i];
loc = i;
}
}
return loc;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TMath::LocMin(Int_t n, Int_t *a)
{
// Return index of array with the minimum element
// If more than one element is minimum returns first found
if (n <= 0) return -1;
Int_t xmin = a[0];
Int_t loc = 0;
for (Int_t i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (xmin > a[i]) {
xmin = a[i];
loc = i;
}
}
return loc;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TMath::LocMin(Int_t n, Float_t *a)
{
// Return index of array with the minimum element
// If more than one element is minimum returns first found
if (n <= 0) return -1;
Float_t xmin = a[0];
Int_t loc = 0;
for (Int_t i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (xmin > a[i]) {
xmin = a[i];
loc = i;
}
}
return loc;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TMath::LocMin(Int_t n, Double_t *a)
{
// Return index of array with the minimum element
// If more than one element is minimum returns first found
if (n <= 0) return -1;
Double_t xmin = a[0];
Int_t loc = 0;
for (Int_t i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (xmin > a[i]) {
xmin = a[i];
loc = i;
}
}
return loc;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TMath::LocMax(Int_t n, Short_t *a)
{
// Return index of array with the maximum element
// If more than one element is maximum returns first found
if (n <= 0) return -1;
Short_t xmax = a[0];
Int_t loc = 0;
for (Int_t i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (xmax < a[i]) {
xmax = a[i];
loc = i;
}
}
return loc;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TMath::LocMax(Int_t n, Int_t *a)
{
// Return index of array with the maximum element
// If more than one element is maximum returns first found
if (n <= 0) return -1;
Int_t xmax = a[0];
Int_t loc = 0;
for (Int_t i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (xmax < a[i]) {
xmax = a[i];
loc = i;
}
}
return loc;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TMath::LocMax(Int_t n, Float_t *a)
{
// Return index of array with the maximum element
// If more than one element is maximum returns first found
if (n <= 0) return -1;
Float_t xmax = a[0];
Int_t loc = 0;
for (Int_t i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (xmax < a[i]) {
xmax = a[i];
loc = i;
}
}
return loc;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TMath::LocMax(Int_t n, Double_t *a)
{
// Return index of array with the maximum element
// If more than one element is maximum returns first found
if (n <= 0) return -1;
Double_t xmax = a[0];
Int_t loc = 0;
for (Int_t i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (xmax < a[i]) {
xmax = a[i];
loc = i;
}
}
return loc;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TMath::BinarySearch(Int_t n, Short_t *array, Short_t value)
{
// Binary search in an array of n values to locate value
//
// Array is supposed to be sorted prior to this call.
// If match is found, function returns position of element.
// If no match found, function gives nearest element smaller than value.
Int_t nabove, nbelow, middle;
nabove = n+1;
nbelow = 0;
while(nabove-nbelow > 1) {
middle = (nabove+nbelow)/2;
if (value == array[middle-1]) return middle-1;
if (value < array[middle-1]) nabove = middle;
else nbelow = middle;
}
return nbelow-1;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TMath::BinarySearch(Int_t n, Short_t **array, Short_t value)
{
// Binary search in an array of n values to locate value
//
// Array is supposed to be sorted prior to this call.
// If match is found, function returns position of element.
// If no match found, function gives nearest element smaller than value.
Int_t nabove, nbelow, middle;
nabove = n+1;
nbelow = 0;
while(nabove-nbelow > 1) {
middle = (nabove+nbelow)/2;
if (value == *array[middle-1]) return middle-1;
if (value < *array[middle-1]) nabove = middle;
else nbelow = middle;
}
return nbelow-1;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TMath::BinarySearch(Int_t n, Int_t *array, Int_t value)
{
// Binary search in an array of n values to locate value
//
// Array is supposed to be sorted prior to this call.
// If match is found, function returns position of element.
// If no match found, function gives nearest element smaller than value.
Int_t nabove, nbelow, middle;
nabove = n+1;
nbelow = 0;
while(nabove-nbelow > 1) {
middle = (nabove+nbelow)/2;
if (value == array[middle-1]) return middle-1;
if (value < array[middle-1]) nabove = middle;
else nbelow = middle;
}
return nbelow-1;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TMath::BinarySearch(Int_t n, Int_t **array, Int_t value)
{
// Binary search in an array of n values to locate value
//
// Array is supposed to be sorted prior to this call.
// If match is found, function returns position of element.
// If no match found, function gives nearest element smaller than value.
Int_t nabove, nbelow, middle;
nabove = n+1;
nbelow = 0;
while(nabove-nbelow > 1) {
middle = (nabove+nbelow)/2;
if (value == *array[middle-1]) return middle-1;
if (value < *array[middle-1]) nabove = middle;
else nbelow = middle;
}
return nbelow-1;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TMath::BinarySearch(Int_t n, Float_t *array, Float_t value)
{
// Binary search in an array of n values to locate value
//
// Array is supposed to be sorted prior to this call.
// If match is found, function returns position of element.
// If no match found, function gives nearest element smaller than value.
Int_t nabove, nbelow, middle;
nabove = n+1;
nbelow = 0;
while(nabove-nbelow > 1) {
middle = (nabove+nbelow)/2;
if (value == array[middle-1]) return middle-1;
if (value < array[middle-1]) nabove = middle;
else nbelow = middle;
}
return nbelow-1;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TMath::BinarySearch(Int_t n, Float_t **array, Float_t value)
{
// Binary search in an array of n values to locate value
//
// Array is supposed to be sorted prior to this call.
// If match is found, function returns position of element.
// If no match found, function gives nearest element smaller than value.
Int_t nabove, nbelow, middle;
nabove = n+1;
nbelow = 0;
while(nabove-nbelow > 1) {
middle = (nabove+nbelow)/2;
if (value == *array[middle-1]) return middle-1;
if (value < *array[middle-1]) nabove = middle;
else nbelow = middle;
}
return nbelow-1;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TMath::BinarySearch(Int_t n, Double_t *array, Double_t value)
{
// Binary search in an array of n values to locate value
//
// Array is supposed to be sorted prior to this call.
// If match is found, function returns position of element.
// If no match found, function gives nearest element smaller than value.
Int_t nabove, nbelow, middle;
nabove = n+1;
nbelow = 0;
while(nabove-nbelow > 1) {
middle = (nabove+nbelow)/2;
if (value == array[middle-1]) return middle-1;
if (value < array[middle-1]) nabove = middle;
else nbelow = middle;
}
return nbelow-1;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TMath::BinarySearch(Int_t n, Double_t **array, Double_t value)
{
// Binary search in an array of n values to locate value
//
// Array is supposed to be sorted prior to this call.
// If match is found, function returns position of element.
// If no match found, function gives nearest element smaller than value.
Int_t nabove, nbelow, middle;
nabove = n+1;
nbelow = 0;
while(nabove-nbelow > 1) {
middle = (nabove+nbelow)/2;
if (value == *array[middle-1]) return middle-1;
if (value < *array[middle-1]) nabove = middle;
else nbelow = middle;
}
return nbelow-1;
}
//_____________________________________________________________________________
void TMath::Sort(Int_t n1, Short_t *a, Int_t *index, Bool_t down)
{
// Sort the n1 elements of the Short_t array a.
// In output the array index contains the indices of the sorted array.
// If down is false sort in increasing order (default is decreasing order).
// This is a translation of the CERNLIB routine sortzv (M101)
// based on the quicksort algorithm.
// NOTE that the array index must be created with a length >= n1
// before calling this function.
Int_t i,i1,n,i2,i3,i33,i222,iswap,n2;
Int_t i22 = 0;
Short_t ai;
n = n1;
if (n <= 0) return;
if (n == 1) {index[0] = 0; return;}
for (i=0;i<n;i++) index[i] = i+1;
for (i1=2;i1<=n;i1++) {
i3 = i1;
i33 = index[i3-1];
ai = a[i33-1];
while(1) {
i2 = i3/2;
if (i2 <= 0) break;
i22 = index[i2-1];
if (ai <= a[i22-1]) break;
index[i3-1] = i22;
i3 = i2;
}
index[i3-1] = i33;
}
while(1) {
i3 = index[n-1];
index[n-1] = index[0];
ai = a[i3-1];
n--;
if(n-1 < 0) {index[0] = i3; break;}
i1 = 1;
while(2) {
i2 = i1+i1;
if (i2 <= n) i22 = index[i2-1];
if (i2-n > 0) {index[i1-1] = i3; break;}
if (i2-n < 0) {
i222 = index[i2];
if (a[i22-1] - a[i222-1] < 0) {
i2++;
i22 = i222;
}
}
if (ai - a[i22-1] > 0) {index[i1-1] = i3; break;}
index[i1-1] = i22;
i1 = i2;
}
}
for (i=0;i<n1;i++) index[i]--;
if (!down) return;
n2 = n1/2;
for (i=0;i<n2;i++) {
iswap = index[i];
index[i] = index[n1-i-1];
index[n1-i-1] = iswap;
}
}
//_____________________________________________________________________________
void TMath::Sort(Int_t n1, Int_t *a, Int_t *index, Bool_t down)
{
// Sort the n1 elements of the Int_t array a.
// In output the array index contains the indices of the sorted array.
// If down is false sort in increasing order (default is decreasing order).
// This is a translation of the CERNLIB routine sortzv (M101)
// based on the quicksort algorithm.
// NOTE that the array index must be created with a length >= n1
// before calling this function.
Int_t i,i1,n,i2,i3,i33,i222,iswap,n2;
Int_t i22 = 0;
Int_t ai;
n = n1;
if (n <= 0) return;
if (n == 1) {index[0] = 0; return;}
for (i=0;i<n;i++) index[i] = i+1;
for (i1=2;i1<=n;i1++) {
i3 = i1;
i33 = index[i3-1];
ai = a[i33-1];
while(1) {
i2 = i3/2;
if (i2 <= 0) break;
i22 = index[i2-1];
if (ai <= a[i22-1]) break;
index[i3-1] = i22;
i3 = i2;
}
index[i3-1] = i33;
}
while(1) {
i3 = index[n-1];
index[n-1] = index[0];
ai = a[i3-1];
n--;
if(n-1 < 0) {index[0] = i3; break;}
i1 = 1;
while(2) {
i2 = i1+i1;
if (i2 <= n) i22 = index[i2-1];
if (i2-n > 0) {index[i1-1] = i3; break;}
if (i2-n < 0) {
i222 = index[i2];
if (a[i22-1] - a[i222-1] < 0) {
i2++;
i22 = i222;
}
}
if (ai - a[i22-1] > 0) {index[i1-1] = i3; break;}
index[i1-1] = i22;
i1 = i2;
}
}
for (i=0;i<n1;i++) index[i]--;
if (!down) return;
n2 = n1/2;
for (i=0;i<n2;i++) {
iswap = index[i];
index[i] = index[n1-i-1];
index[n1-i-1] = iswap;
}
}
//_____________________________________________________________________________
void TMath::Sort(Int_t n1, Float_t *a, Int_t *index, Bool_t down)
{
// Sort the n1 elements of the Float_t array a.
// In output the array index contains the indices of the sorted array.
// If down is false sort in increasing order (default is decreasing order).
// This is a translation of the CERNLIB routine sortzv (M101)
// based on the quicksort algorithm.
// NOTE that the array index must be created with a length >= n1
// before calling this function.
Int_t i,i1,n,i2,i3,i33,i222,iswap,n2;
Int_t i22 = 0;
Float_t ai;
n = n1;
if (n <= 0) return;
if (n == 1) {index[0] = 0; return;}
for (i=0;i<n;i++) index[i] = i+1;
for (i1=2;i1<=n;i1++) {
i3 = i1;
i33 = index[i3-1];
ai = a[i33-1];
while(1) {
i2 = i3/2;
if (i2 <= 0) break;
i22 = index[i2-1];
if (ai <= a[i22-1]) break;
index[i3-1] = i22;
i3 = i2;
}
index[i3-1] = i33;
}
while(1) {
i3 = index[n-1];
index[n-1] = index[0];
ai = a[i3-1];
n--;
if(n-1 < 0) {index[0] = i3; break;}
i1 = 1;
while(2) {
i2 = i1+i1;
if (i2 <= n) i22 = index[i2-1];
if (i2-n > 0) {index[i1-1] = i3; break;}
if (i2-n < 0) {
i222 = index[i2];
if (a[i22-1] - a[i222-1] < 0) {
i2++;
i22 = i222;
}
}
if (ai - a[i22-1] > 0) {index[i1-1] = i3; break;}
index[i1-1] = i22;
i1 = i2;
}
}
for (i=0;i<n1;i++) index[i]--;
if (!down) return;
n2 = n1/2;
for (i=0;i<n2;i++) {
iswap = index[i];
index[i] = index[n1-i-1];
index[n1-i-1] = iswap;
}
}
//_____________________________________________________________________________
void TMath::Sort(Int_t n1, Double_t *a, Int_t *index, Bool_t down)
{
// Sort the n1 elements of the Double_t array a.
// In output the array index contains the indices of the sorted array.
// If down is false sort in increasing order (default is decreasing order).
// This is a translation of the CERNLIB routine sortzv (M101)
// based on the quicksort algorithm.
// NOTE that the array index must be created with a length >= n1
// before calling this function.
Int_t i,i1,n,i2,i3,i33,i222,iswap,n2;
Int_t i22 = 0;
Double_t ai;
n = n1;
if (n <= 0) return;
if (n == 1) {index[0] = 0; return;}
for (i=0;i<n;i++) index[i] = i+1;
for (i1=2;i1<=n;i1++) {
i3 = i1;
i33 = index[i3-1];
ai = a[i33-1];
while(1) {
i2 = i3/2;
if (i2 <= 0) break;
i22 = index[i2-1];
if (ai <= a[i22-1]) break;
index[i3-1] = i22;
i3 = i2;
}
index[i3-1] = i33;
}
while(1) {
i3 = index[n-1];
index[n-1] = index[0];
ai = a[i3-1];
n--;
if(n-1 < 0) {index[0] = i3; break;}
i1 = 1;
while(2) {
i2 = i1+i1;
if (i2 <= n) i22 = index[i2-1];
if (i2-n > 0) {index[i1-1] = i3; break;}
if (i2-n < 0) {
i222 = index[i2];
if (a[i22-1] - a[i222-1] < 0) {
i2++;
i22 = i222;
}
}
if (ai - a[i22-1] > 0) {index[i1-1] = i3; break;}
index[i1-1] = i22;
i1 = i2;
}
}
for (i=0;i<n1;i++) index[i]--;
if (!down) return;
n2 = n1/2;
for (i=0;i<n2;i++) {
iswap = index[i];
index[i] = index[n1-i-1];
index[n1-i-1] = iswap;
}
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
ULong_t TMath::Hash(const void *txt, Int_t ntxt)
{
// Calculates hash index from any char string
// based on precalculated table of 256 specially selected
// random numbers.
//
// For string: i = TExMap::Hash(string,nstring);
// For int: i = TExMap::Hash(&intword,sizeof(int));
// For pointer: i = TExMap::Hash(&pointer,sizeof(void*));
//
// Limitation: for ntxt>256 calculates hash only from first 256 bytes
//
// V.Perev
const UChar_t *uc = (const UChar_t*) txt;
ULong_t u = 0, uu = 0;
static ULong_t utab[256] =
{0xb93f6fc0,0x553dfc51,0xb22c1e8c,0x638462c0,0x13e81418,0x2836e171,0x7c4abb90,0xda1a4f39
,0x38f211d1,0x8c804829,0x95a6602d,0x4c590993,0x1810580a,0x721057d4,0x0f587215,0x9f49ce2a
,0xcd5ab255,0xab923a99,0x80890f39,0xbcfa2290,0x16587b52,0x6b6d3f0d,0xea8ff307,0x51542d5c
,0x189bf223,0x39643037,0x0e4a326a,0x214eca01,0x47645a9b,0x0f364260,0x8e9b2da4,0x5563ebd9
,0x57a31c1c,0xab365854,0xdd63ab1f,0x0b89acbd,0x23d57d33,0x1800a0fd,0x225ac60a,0xd0e51943
,0x6c65f669,0xcb966ea0,0xcbafda95,0x2e5c0c5f,0x2988e87e,0xc781cbab,0x3add3dc7,0x693a2c30
,0x42d6c23c,0xebf85f26,0x2544987e,0x2e315e3f,0xac88b5b5,0x7ebd2bbb,0xda07c87b,0x20d460f1
,0xc61c3f40,0x182046e7,0x3b6c3b66,0x2fc10d4a,0x0780dfbb,0xc437280c,0x0988dd07,0xe1498606
,0x8e61d728,0x4f1f3909,0x040a9682,0x49411b29,0x391b0e1c,0xd7905241,0xdd77d95b,0x88426c13
,0x33033e58,0xe158e30e,0x7e342647,0x1e09544b,0x4637353d,0x18ea0924,0x39212b08,0x12580ae8
,0x269a6f06,0x3e10b73b,0x123db33b,0x085412da,0x3bb5f464,0xd9b2d442,0x103d26bb,0xd0038bab
,0x45b6177f,0xfb48f1fe,0x99074c55,0xb545e82e,0x5f79fd0d,0x570f3ae4,0x57e43255,0x037a12ae
,0x4357bdb2,0x337c2c4d,0x2982499d,0x2ab72793,0x3900e7d1,0x57a6bb81,0x7503609b,0x3f39c0d0
,0x717b389d,0x5748034f,0x4698162b,0x5801b97c,0x1dfd5d7e,0xc1386d1c,0xa387a72a,0x084547e4
,0x2e54d8e9,0x2e2f384c,0xe09ccc20,0x8904b71e,0x3e24edc5,0x06a22e16,0x8a2be1df,0x9e5058b2
,0xe01a2f16,0x03325eed,0x587ecfe6,0x584d9cd3,0x32926930,0xe943d68c,0xa9442da8,0xf9650560
,0xf003871e,0x1109c663,0x7a2f2f89,0x1c2210bb,0x37335787,0xb92b382f,0xea605cb5,0x336bbe38
,0x08126bd3,0x1f8c2bd6,0xba6c46f2,0x1a4d1b83,0xc988180d,0xe2582505,0xa8a1b375,0x59a08c49
,0x3db54b48,0x44400f35,0x272d4e7f,0x5579f733,0x98eb590e,0x8ee09813,0x12cc9301,0xc85c402d
,0x135c1039,0x22318128,0x4063c705,0x87a8a3fa,0xfc14431f,0x6e27bf47,0x2d080a19,0x01dba174
,0xe343530b,0xaa1bfced,0x283bb2c8,0x5df250c8,0x4ff9140b,0x045039c1,0xa377780d,0x750f2661
,0x2b108918,0x0b152120,0x3cbc251f,0x5e87b350,0x060625bb,0xe068ba3b,0xdb73ebd7,0x66014ff3
,0xdb003000,0x161a3a0b,0xdc24e142,0x97ea5575,0x635a3cab,0xa719100a,0x256084db,0xc1f4a1e7
,0xe13388f2,0xb8199fc9,0x50c70dc9,0x08154211,0xd60e5220,0xe52c6592,0x584c5fe1,0xfe5e0875
,0x21072b30,0x3370d773,0x92608fe2,0x2d013d93,0x53414b3c,0x2c066142,0x64676644,0x0420887c
,0x35c01187,0x6822119b,0xf9bfe6df,0x273f4ee4,0x87973149,0x7b41282d,0x635d0d1f,0x5f7ecc1e
,0x14c3608a,0x462dfdab,0xc33d8808,0x1dcd995e,0x0fcb11ba,0x11755914,0x5a62044b,0x37f76755
,0x345bd058,0x8831c2b5,0x204a8468,0x3b0b1cd2,0x444e56f4,0x97a93e2c,0xd5f15067,0x266a95fa
,0xff4f8036,0x6160060d,0x930c472f,0xed922184,0x37120251,0xc0add74f,0x1c0bc89d,0x018d47f2
,0xff59ef66,0xd1901a17,0x91f6701b,0x0960082f,0x86f6a8f3,0x1154fecd,0x9867d1de,0x0945482f
,0x790ffcac,0xe5610011,0x4765637e,0xa745dbff,0x841fdcb3,0x4f7372a0,0x3c05013d,0xf1ac4ab7
,0x3bc5b5cc,0x49a73349,0x356a7f67,0x1174f031,0x11d32634,0x4413d301,0x1dd285c4,0x3fae4800
};
ntxt &= 255;
for ( ; ntxt--; uc++) {
uu = uu<<1 ^ utab[(*uc) ^ ntxt];
u ^= uu;
}
return u;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
ULong_t TMath::Hash(const char *txt)
{
return Hash(txt, Int_t(strlen(txt)));
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::BesselI0(Double_t x)
{
// Computation of the modified Bessel function I_0(x) for any real x.
//
// The algorithm is based on the article by Abramowitz and Stegun [1]
// as denoted in Numerical Recipes 2nd ed. on p. 230 (W.H.Press et al.).
//
// [1] M.Abramowitz and I.A.Stegun, Handbook of Mathematical Functions,
// Applied Mathematics Series vol. 55 (1964), Washington.
//
//--- NvE 12-mar-2000 UU-SAP Utrecht
// Parameters of the polynomial approximation
const Double_t p1=1.0, p2=3.5156229, p3=3.0899424,
p4=1.2067492, p5=0.2659732, p6=3.60768e-2, p7=4.5813e-3;
const Double_t q1= 0.39894228, q2= 1.328592e-2, q3= 2.25319e-3,
q4=-1.57565e-3, q5= 9.16281e-3, q6=-2.057706e-2,
q7= 2.635537e-2, q8=-1.647633e-2, q9= 3.92377e-3;
Double_t ax = TMath::Abs(x);
Double_t y=0, result=0;
if (ax < 3.75) {
y = pow(x/3.75,2);
result = p1+y*(p2+y*(p3+y*(p4+y*(p5+y*(p6+y*p7)))));
} else {
y = 3.75/ax;
result = (exp(ax)/sqrt(ax))*(q1+y*(q2+y*(q3+y*(q4+y*(q5+y*(q6+y*(q7+y*(q8+y*q9))))))));
}
return result;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::BesselK0(Double_t x)
{
// Computation of the modified Bessel function K_0(x) for positive real x.
//
// The algorithm is based on the article by Abramowitz and Stegun [1]
// as denoted in Numerical Recipes 2nd ed. on p. 230 (W.H.Press et al.).
//
// [1] M.Abramowitz and I.A.Stegun, Handbook of Mathematical Functions,
// Applied Mathematics Series vol. 55 (1964), Washington.
//
//--- NvE 12-mar-2000 UU-SAP Utrecht
// Parameters of the polynomial approximation
const Double_t p1=-0.57721566, p2=0.42278420, p3=0.23069756,
p4= 3.488590e-2, p5=2.62698e-3, p6=1.0750e-4, p7=7.4e-5;
const Double_t q1= 1.25331414, q2=-7.832358e-2, q3= 2.189568e-2,
q4=-1.062446e-2, q5= 5.87872e-3, q6=-2.51540e-3, q7=5.3208e-4;
if (x <= 0) {
printf(" *K0* Invalid argument x = %gn",x);
return 0;
}
Double_t y=0,result=0;
if (x <= 2) {
y = x*x/4.;
result = (-log(x/2.)*TMath::BesselI0(x))+(p1+y*(p2+y*(p3+y*(p4+y*(p5+y*(p6+y*p7))))));
} else {
y = 2./x;
result = (exp(-x)/sqrt(x))*(q1+y*(q2+y*(q3+y*(q4+y*(q5+y*(q6+y*q7))))));
}
return result;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::BesselI1(Double_t x)
{
// Computation of the modified Bessel function I_1(x) for any real x.
//
// The algorithm is based on the article by Abramowitz and Stegun [1]
// as denoted in Numerical Recipes 2nd ed. on p. 230 (W.H.Press et al.).
//
// [1] M.Abramowitz and I.A.Stegun, Handbook of Mathematical Functions,
// Applied Mathematics Series vol. 55 (1964), Washington.
//
//--- NvE 12-mar-2000 UU-SAP Utrecht
// Parameters of the polynomial approximation
const Double_t p1=0.5, p2=0.87890594, p3=0.51498869,
p4=0.15084934, p5=2.658733e-2, p6=3.01532e-3, p7=3.2411e-4;
const Double_t q1= 0.39894228, q2=-3.988024e-2, q3=-3.62018e-3,
q4= 1.63801e-3, q5=-1.031555e-2, q6= 2.282967e-2,
q7=-2.895312e-2, q8= 1.787654e-2, q9=-4.20059e-3;
Double_t ax = TMath::Abs(x);
Double_t y=0, result=0;
if (ax < 3.75) {
y = pow(x/3.75,2);
result = x*(p1+y*(p2+y*(p3+y*(p4+y*(p5+y*(p6+y*p7))))));
} else {
y = 3.75/ax;
result = (exp(ax)/sqrt(ax))*(q1+y*(q2+y*(q3+y*(q4+y*(q5+y*(q6+y*(q7+y*(q8+y*q9))))))));
if (x < 0) result = -result;
}
return result;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::BesselK1(Double_t x)
{
// Computation of the modified Bessel function K_1(x) for positive real x.
//
// The algorithm is based on the article by Abramowitz and Stegun [1]
// as denoted in Numerical Recipes 2nd ed. on p. 230 (W.H.Press et al.).
//
// [1] M.Abramowitz and I.A.Stegun, Handbook of Mathematical Functions,
// Applied Mathematics Series vol. 55 (1964), Washington.
//
//--- NvE 12-mar-2000 UU-SAP Utrecht
// Parameters of the polynomial approximation
const Double_t p1= 1., p2= 0.15443144, p3=-0.67278579,
p4=-0.18156897, p5=-1.919402e-2, p6=-1.10404e-3, p7=-4.686e-5;
const Double_t q1= 1.25331414, q2= 0.23498619, q3=-3.655620e-2,
q4= 1.504268e-2, q5=-7.80353e-3, q6= 3.25614e-3, q7=-6.8245e-4;
if (x <= 0) {
printf(" *K1* Invalid argument x = %gn",x);
return 0;
}
Double_t y=0,result=0;
if (x <= 2) {
y = x*x/4.;
result = (log(x/2.)*TMath::BesselI1(x))+(1./x)*(p1+y*(p2+y*(p3+y*(p4+y*(p5+y*(p6+y*p7))))));
} else {
y = 2./x;
result = (exp(-x)/sqrt(x))*(q1+y*(q2+y*(q3+y*(q4+y*(q5+y*(q6+y*q7))))));
}
return result;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::BesselK(Int_t n,Double_t x)
{
// Computation of the Integer Order Modified Bessel function K_n(x)
// for n=0,1,2,... and positive real x.
//
// The algorithm uses the recurrence relation
//
// K_n+1(x) = (2n/x)*K_n(x) + K_n-1(x)
//
// as denoted in Numerical Recipes 2nd ed. on p. 232 (W.H.Press et al.).
//
//--- NvE 12-mar-2000 UU-SAP Utrecht
if (x <= 0 || n < 0) {
printf(" *K* Invalid argument(s) (n,x) = (%d, %g)n",n,x);
return 0;
}
if (n==0) return TMath::BesselK0(x);
if (n==1) return TMath::BesselK1(x);
// Perform upward recurrence for all x
Double_t tox = 2./x;
Double_t bkm = TMath::BesselK0(x);
Double_t bk = TMath::BesselK1(x);
Double_t bkp = 0;
for (Int_t j=1; j<n; j++) {
bkp = bkm+Double_t(j)*tox*bk;
bkm = bk;
bk = bkp;
}
return bk;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::BesselI(Int_t n,Double_t x)
{
// Computation of the Integer Order Modified Bessel function I_n(x)
// for n=0,1,2,... and any real x.
//
// The algorithm uses the recurrence relation
//
// I_n+1(x) = (-2n/x)*I_n(x) + I_n-1(x)
//
// as denoted in Numerical Recipes 2nd ed. on p. 232 (W.H.Press et al.).
//
//--- NvE 12-mar-2000 UU-SAP Utrecht
Int_t iacc = 40; // Increase to enhance accuracy
Double_t bigno = 1.e10, bigni = 1.e-10;
if (n < 0) {
printf(" *I* Invalid argument (n,x) = (%d, %g)n",n,x);
return 0;
}
if (n==0) return TMath::BesselI0(x);
if (n==1) return TMath::BesselI1(x);
if (TMath::Abs(x) < 1.e-10) return 0;
Double_t tox = 2./TMath::Abs(x);
Double_t bip = 0,bim = 0;
Double_t bi = 1;
Double_t result = 0;
Int_t m = 2*((n+Int_t(sqrt(Float_t(iacc*n))))); // Downward recurrence from even m
for (Int_t j=m; j<=1; j--) {
bim = bip+Double_t(j)*tox*bi;
bip = bi;
bi = bim;
// Renormalise to prevent overflows
if (TMath::Abs(bi) > bigno) {
result *= bigni;
bi *= bigni;
bip *= bigni;
}
if (j==n) result=bip;
}
result *= TMath::BesselI0(x)/bi; // Normalise with BesselI0(x)
if ((x < 0) && (n%2 == 1)) result = -result;
return result;
}